Ovarian ferroptosis induced by androgen is involved in pathogenesis of PCOS
- PMID: 38550897
- PMCID: PMC10973940
- DOI: 10.1093/hropen/hoae013
Ovarian ferroptosis induced by androgen is involved in pathogenesis of PCOS
Abstract
Study question: Does ovarian ferroptosis play an active role in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)?
Summary answer: Increased ovarian ferroptosis was present in PCOS ovaries and the inhibition of ferroptosis with ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1) ameliorated polycystic ovary morphology and anovulation.
What is known already: Programmed cell death plays a fundamental role in ovarian follicle development. However, the types and mechanisms of cell death involved in the ovary are yet to be elucidated. Ferroptosis is a recently discovered iron-dependent programmed cell death. Impaired iron metabolism and cell death have been observed in women with PCOS, the main cause of anovulatory infertility. Additionally, previous studies reported that an abnormal expression of noncoding RNA may promote ferroptosis in immortalized ovarian granulosa cell lines. However, little is known about whether ovarian ferroptosis is increased in PCOS, and there is insufficient direct evidence for a role of ferroptosis in PCOS, and the underlying mechanism. Moreover, the effect of the inhibition of ferroptosis with Fer-1 in PCOS remains unclear.
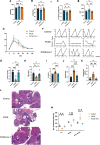
Study design size duration: Ferroptosis was evaluated in human granulosa cells (hGCs) from non-PCOS (n = 6-16) and PCOS (n = 7-18) patients. The experimental study was completed in vitro using primary hGCs from women undergoing IVF. Improvements in PCOS indicators following ferroptosis inhibition with Fer-1 were investigated in a dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)-induced PCOS rat model (n = 8 per group).
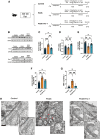
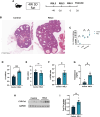
Participants/materials setting methods: Ovarian ferroptosis was evaluated in the following ways: by detecting iron concentrations via ELISA and fluorescent probes; measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) concentrations via ELISA; assessing ferroptosis-related protein abundance with western blotting; observing mitochondrial morphology with transmission electron microscopy; and determining cell viability. Primary hGCs were collected from women undergoing IVF. They were treated with dihydrotestosterone (DHT) for 24 h. The effect of DHT on ferroptosis was examined in the presence or absence of small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown of the putative receptor coregulator for signaling molecules. The role of ovarian ferroptosis in PCOS progression was explored in vivo in rats. The DHEA-induced PCOS rat model was treated with the ferroptosis inhibitor, Fer-1, and the oocytes and metaphase II oocytes were counted after ovarian stimulation. Additionally, rats were treated with the ferroptosis inducer, RSL3, to further explore the effect of ferroptosis. The concentrations of testosterone, FSH, and LH were assessed.
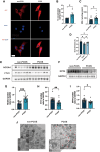
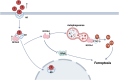
Main results and the role of chance: Increased ferroptosis was detected in the ovaries of patients with PCOS and in rats with DHEA-induced PCOS. Increased concentrations of Fe2+ (P < 0.05) and MDA (P < 0.05), and upregulated nuclear receptor coactivator 4 protein levels, and downregulated ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) proteins were observed in the hGCs in patients with PCOS and ovaries of PCOS rats (P < 0.05 versus control). DHT was shown to induce ferroptosis via activation of NOCA4-dependent ferritinophagy. The inhibition of ferroptosis with Fer-1 in rats ameliorated a cluster of PCOS traits including impaired glucose tolerance, irregular estrous cycles, reproductive hormone dysfunction, hyperandrogenism, polycystic ovaries, anovulation, and oocyte quality (P < 0.05). Treating rats with RSL3 resulted in polycystic ovaries and hyperandrogenism (P < 0.05).
Large-scale data: N/A.
Limitations reasons for caution: Although ovarian-targeted ferroptosis inhibition may be a more targeted treatment for PCOS, the underlying mechanisms in the cycle between ferroptosis and hyperandrogenism require further exploration. Additionally, since PCOS shows high heterogeneity, it is important to investigate whether ferroptosis increases are present in all patients with PCOS.
Wider implications of the findings: Androgen-induced ovarian ferroptosis appears to play a role in the pathogenesis of PCOS, which potentially makes it a promising treatment target in PCOS.
Study funding/competing interests: This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFC2705500, 2023YFC2705505, 2019YFA0802604), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82130046, 82320108009, 82101708, 82101747, and 82001517), Shanghai leading talent program, Innovative research team of high-level local universities in Shanghai (No. SHSMU-ZLCX20210201, No. SSMU-ZLCX20180401), Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Affiliated Renji Hospital Clinical Research Innovation Cultivation Fund Program (RJPY-DZX-003) and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission-Gaofeng Clinical Medicine Grant Support (No. 20161413), Shanghai's Top Priority Research Center Construction Project (2023ZZ02002), and Three-Year Action Plan for Strengthening the Construction of the Public Health System in Shanghai (GWVI-11.1-36). The authors report no competing interests.
Keywords: PCOS; androgen; ferroptosis; nuclear receptor coactivator 4; ovarian dysfunction.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest in relation to this work.
Figures



References
-
- Azziz R, Carmina E, Chen Z, Dunaif A, Laven JSE, Legro RS, Lizneva D, Natterson-Horowtiz B, Teede HJ, Yildiz BO.. Polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2016;2:16057. - PubMed
-
- Bannigida DM, Nayak BS, Vijayaraghavan R.. Insulin resistance and oxidative marker in women with PCOS. Arch Physiol Biochem 2020;126:183–186. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
