The motive forces in DNA-enabled nanomachinery
- PMID: 38551008
- PMCID: PMC10973203
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109453
The motive forces in DNA-enabled nanomachinery
Abstract
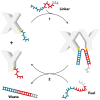
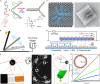
Building machines that can augment or replace human efforts to accomplish complex tasks is one of central topics for humanity. Especially, nanomachines made of discrete numbers of molecular components can perform intended mechanical movements in a predetermined manner. Utilizing free energies of Watson-Crick base pairing, different types of DNA nanomachines have been invented to operate intended stepwise or autonomous actions with external stimuli, and we here summarized the motive forces that drive DNA-based nanomachineries. DNA tweezers, DNA origami actuators, DNA walkers, and DNA machine-enabled bulk sensing are discussed including structural motif design, toehold creations for strands displacement reactions, and other input forces, as well as examples of biological motor-driven hybrid nanomachines. By addressing these prototypical artificial nanodevices, we envision future focuses should include developing various input energies, host cell-assisted structure self-replication, and nonequilibrium transportations.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Supramolecular chemistry.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Yurke B. Using DNA to Power Nanostructures. Genet. Program. Evolvable Mach. 2003;4:111–122. doi: 10.1023/A:1023928811651. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

