Role of RNA binding proteins of the Drosophila behavior and human splicing (DBHS) family in health and cancer
- PMID: 38551131
- PMCID: PMC10984136
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2024.2332855
Role of RNA binding proteins of the Drosophila behavior and human splicing (DBHS) family in health and cancer
Abstract
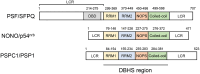
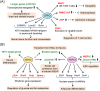
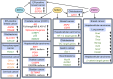
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) play crucial roles in the functions and homoeostasis of various tissues by regulating multiple events of RNA processing including RNA splicing, intracellular RNA transport, and mRNA translation. The Drosophila behavior and human splicing (DBHS) family proteins including PSF/SFPQ, NONO, and PSPC1 are ubiquitously expressed RBPs that contribute to the physiology of several tissues. In mammals, DBHS proteins have been reported to contribute to neurological diseases and play crucial roles in cancers, such as prostate, breast, and liver cancers, by regulating cancer-specific gene expression. Notably, in recent years, multiple small molecules targeting DBHS family proteins have been developed for application as cancer therapeutics. This review provides a recent overview of the functions of DBHS family in physiology and pathophysiology, and discusses the application of DBHS family proteins as promising diagnostic and therapeutic targets for cancers.
Keywords: DBHS family; NONO; PSF/SFPQ; PSPC1; cancers; neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural plasticity of the coiled-coil interactions in human SFPQ.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 11;53(2):gkae1198. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1198. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39698821 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of a SFPQ/PSPC1 heterodimer provides insights into preferential heterodimerization of human DBHS family proteins.J Biol Chem. 2018 Apr 27;293(17):6593-6602. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001451. Epub 2018 Mar 12. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29530979 Free PMC article.
-
Paraspeckle subnuclear bodies depend on dynamic heterodimerisation of DBHS RNA-binding proteins via their structured domains.J Biol Chem. 2022 Nov;298(11):102563. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102563. Epub 2022 Oct 7. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 36209820 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of the RNA-Binding Protein SFPQ in Neuronal Function and Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 28;21(19):7151. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197151. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32998269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paraspeckles: nuclear bodies built on long noncoding RNA.J Cell Biol. 2009 Sep 7;186(5):637-44. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200906113. Epub 2009 Aug 31. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19720872 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An N-terminal and ankyrin repeat domain interactome of Shank3 identifies the protein complex with the splicing regulator Nono in mice.Genes Cells. 2024 Sep;29(9):746-756. doi: 10.1111/gtc.13142. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Genes Cells. 2024. PMID: 38964745 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Immunoregulation: harnessing CircRNAs and PiRNAs to Amplify PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibition Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 May 28;19:4803-4834. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S461289. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38828205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural plasticity of the coiled-coil interactions in human SFPQ.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 11;53(2):gkae1198. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1198. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39698821 Free PMC article.
-
The implication of non-AUG-initiated N-terminally extended proteoforms in cancer.RNA Biol. 2025 Dec;22(1):1-18. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2025.2498203. Epub 2025 Apr 29. RNA Biol. 2025. PMID: 40276932 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Splicing in Tumorigenesis and Cancer Therapy.Biomolecules. 2025 May 29;15(6):789. doi: 10.3390/biom15060789. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563429 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
