Loss of GABARAP mediates resistance to immunogenic chemotherapy in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 38551812
- PMCID: PMC11830986
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2023022777
Loss of GABARAP mediates resistance to immunogenic chemotherapy in multiple myeloma
Abstract
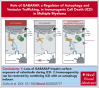
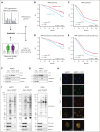
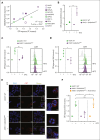
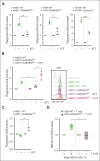
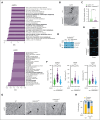
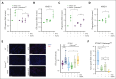
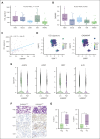
Immunogenic cell death (ICD) is a form of cell death by which cancer treatments can induce a clinically relevant antitumor immune response in a broad range of cancers. In multiple myeloma (MM), the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib is an ICD inducer and creates durable therapeutic responses in patients. However, eventual relapse and resistance to bortezomib appear inevitable. Here, by integrating patient transcriptomic data with an analysis of calreticulin (CRT) protein interactors, we found that GABA type A receptor-associated protein (GABARAP) is a key player whose loss prevented tumor cell death from being perceived as immunogenic after bortezomib treatment. GABARAP is located on chromosome 17p, which is commonly deleted in patients with high risk MM. GABARAP deletion impaired the exposure of the eat-me signal CRT on the surface of dying MM cells in vitro and in vivo, thus reducing tumor cell phagocytosis by dendritic cells and the subsequent antitumor T-cell response. Low GABARAP was independently associated with shorter survival in patients with MM and reduced tumor immune infiltration. Mechanistically, we found that GABARAP deletion blocked ICD signaling by decreasing autophagy and altering Golgi apparatus morphology, with consequent defects in the downstream vesicular transport of CRT. Conversely, upregulating autophagy using rapamycin restored Golgi morphology, CRT exposure, and ICD signaling in GABARAPKO cells undergoing bortezomib treatment. Therefore, coupling an ICD inducer, such as bortezomib, with an autophagy inducer, such as rapamycin, may improve patient outcomes in MM, in which low GABARAP in the form of del(17p) is common and leads to worse outcomes.
© 2024 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: N.C.M. serves on advisory boards of and as consultant to Takeda, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Amgen, AbbVie, Oncopep, Karyopharm, Adaptive Biotechnology, and Novartis; and holds equity ownership in Oncopep. K.C.A. is a consultant for Janssen, Pfizer, and AstraZeneca; and serves as a board member with equity ownership in Oncopep, C4Therapeutics, Starton, NextRNA, Window, and Dynamic Cell Therapies. A.G. and K.C.A filed a provisional patent on the role of GABARAP as modulator of ICD. M.K.S. is a consultant for AbbVie and serves as advisor for Neuberg Center for Genomic Medicine. G.B. is a consultant for Prothena. D.C. has equity ownership in C4 Therapeutics outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Immunogenic therapy: new actors in myeloma.Blood. 2024 Jun 20;143(25):2564-2565. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024024709. Blood. 2024. PMID: 38900472 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sistigu A, Yamazaki T, Vacchelli E, et al. Cancer cell-autonomous contribution of type I interferon signaling to the efficacy of chemotherapy. Nat Med. 2014;20(11):1301–1309. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Zitvogel L. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol. 2013;31:51–72. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer G, Galassi C, Zitvogel L, Galluzzi L. Immunogenic cell stress and death. Nat Immunol. 2022;23(4):487–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

