BRCA1-Mediated Dual Regulation of Ferroptosis Exposes a Vulnerability to GPX4 and PARP Co-Inhibition in BRCA1-Deficient Cancers
- PMID: 38552003
- PMCID: PMC11296921
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-1220
BRCA1-Mediated Dual Regulation of Ferroptosis Exposes a Vulnerability to GPX4 and PARP Co-Inhibition in BRCA1-Deficient Cancers
Abstract
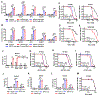
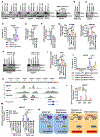
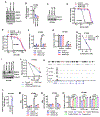
Resistance to poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPi) limits the therapeutic efficacy of PARP inhibition in treating breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1)-deficient cancers. Here we reveal that BRCA1 has a dual role in regulating ferroptosis. BRCA1 promotes the transcription of voltage-dependent anion channel 3 (VDAC3) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4); consequently, BRCA1 deficiency promotes cellular resistance to erastin-induced ferroptosis but sensitizes cancer cells to ferroptosis induced by GPX4 inhibitors (GPX4i). In addition, nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4)-mediated ferritinophagy and defective GPX4 induction unleash potent ferroptosis in BRCA1-deficient cancer cells upon PARPi and GPX4i co-treatment. Finally, we show that xenograft tumors derived from patients with BRCA1-mutant breast cancer with PARPi resistance exhibit decreased GPX4 expression and high sensitivity to PARP and GPX4 co-inhibition. Our results show that BRCA1 deficiency induces a ferroptosis vulnerability to PARP and GPX4 co-inhibition and inform a therapeutic strategy for overcoming PARPi resistance in BRCA1-deficient cancers. Significance: BRCA1 deficiency promotes resistance to erastin-induced ferroptosis via blocking VDAC3 yet renders cancer cells vulnerable to GPX4i-induced ferroptosis via inhibiting GPX4. NCOA4 induction and defective GPX4 further synergizes GPX4i with PARPi to induce ferroptosis in BRCA1-deficient cancers and targeting GPX4 mitigates PARPi resistance in those cancers. See related commentary by Alborzinia and Friedmann Angeli, p. 1372.
©2024 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
B.G. and G.L. have filed a patent application relating to the use of GPX4 inhibitors in combination with PARP inhibitors for treating
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA016672/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- NSTC 112-2639-B-039-001-ASP/National Science and Technology Council (NSTC)
- Boot Walk Seed Award from Radiation Oncology Strategic Initiatives at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
- NSTC 113-2634-F-039-001/T-STAR Center
- VC2020-001/V Foundation
- The N.G. and Helen T. Hawkins Distinguished Professorship for Cancer Research of MD Anderson Cancer Center
- R01 CA255074/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Research Center Program from the Ministry of Education in Taiwan
- R01CA255074/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U54 CA274220/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA269646/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- W81XWH2210504_BC211174/U.S. Department of Defense (DOD)
- RP210028/CPRIT Research Training Award CPRIT Training Program
- Institutional Research Fund and Bridge Fund from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
- R01CA181196/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 CA244144/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA247992/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RP220258/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT)
- R01 CA181196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

