Time elapsed from definitive diagnosis to surgery for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a nationwide observational study in Japan
- PMID: 38553078
- PMCID: PMC10982743
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-082342
Time elapsed from definitive diagnosis to surgery for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a nationwide observational study in Japan
Abstract
Objectives: This study documents the time elapsed from the diagnosis of osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH) to surgery, exploring the factors that influence ONFH severity.
Design: Retrospective observational study of a nationwide database.
Setting: The Kaplan-Meier method with log-rank tests was applied to examine the period from definitive diagnosis of ONFH to surgery using any surgery as the end point. For bilateral cases, the date of the first surgery was the endpoint.
Participants: This study included 2074 ONFH cases registered in 34 university hospitals and highly specialised hospitals of the multicentre sentinel monitoring system of the Japanese Investigation Committee between 1997 and 2018.
Main outcome measure: The primary outcome was the time from diagnosis to surgery. The secondary outcome was the proportion of subjects remaining without surgery at 3, 6 and 9 months, and at 1, 2 and 5 years after diagnosis.
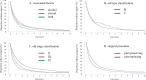
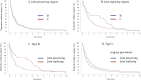
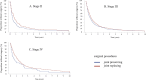
Results: The median time to surgery was 9 months (IQR 4-22 months) after diagnosis of ONFH. The time to surgery was significantly shorter in the alcohol alone group and the combined corticosteroid and alcohol group than in the corticosteroid alone group (p=0.018 and p<0.001, respectively), in early stage ONFH with no or mild joint destruction (stages II and III, p<0.001), and with joint preserving surgery (p<0.001). The proportion without surgery was 75.8% at 3 months, 59.6% at 6 months, 48.2% at 9 months, 40.5% at 1 year, 22.2% at 2 years and 8.3% at 5 years.
Conclusion: ONFH has been considered to be an intractable disease that often requires surgical treatment, but the fact that surgery was performed in more than half of the patients within 9 months from diagnosis suggests severe disease with a significant clinical impact.
Trial registration number: Chiba University ID1049.
Keywords: EPIDEMIOLOGY; Factor Analysis, Statistical; Hip; REGISTRIES; RHEUMATOLOGY.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
