Genotype-phenotype correlation in PRKN-associated Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 38553467
- PMCID: PMC10980707
- DOI: 10.1038/s41531-024-00677-3
Genotype-phenotype correlation in PRKN-associated Parkinson's disease
Abstract
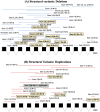
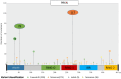
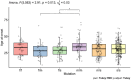
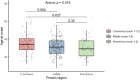
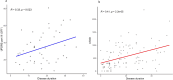
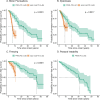
Bi-allelic pathogenic variants in PRKN are the most common cause of autosomal recessive Parkinson's disease (PD). 647 patients with PRKN-PD were included in this international study. The pathogenic variants present were characterised and investigated for their effect on phenotype. Clinical features and progression of PRKN-PD was also assessed. Among 133 variants in index cases (n = 582), there were 58 (43.6%) structural variants, 34 (25.6%) missense, 20 (15%) frameshift, 10 splice site (7.5%%), 9 (6.8%) nonsense and 2 (1.5%) indels. The most frequent variant overall was an exon 3 deletion (n = 145, 12.3%), followed by the p.R275W substitution (n = 117, 10%). Exon3, RING0 protein domain and the ubiquitin-like protein domain were mutational hotspots with 31%, 35.4% and 31.7% of index cases presenting mutations in these regions respectively. The presence of a frameshift or structural variant was associated with a 3.4 ± 1.6 years or a 4.7 ± 1.6 years earlier age at onset of PRKN-PD respectively (p < 0.05). Furthermore, variants located in the N-terminus of the protein, a region enriched with frameshift variants, were associated with an earlier age at onset. The phenotype of PRKN-PD was characterised by slow motor progression, preserved cognition, an excellent motor response to levodopa therapy and later development of motor complications compared to early-onset PD. Non-motor symptoms were however common in PRKN-PD. Our findings on the relationship between the type of variant in PRKN and the phenotype of the disease may have implications for both genetic counselling and the design of precision clinical trials.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.D.F. received honoraria for participating as scientifica board member to advisory board from Sanofi, Bial, Zambon. H.M. is employed by UCL. In the last 12 months he reports paid consultancy from Roche, Aprinoia and Amylyx; lecture fees/honoraria—BMJ, Kyowa Kirin, Movement Disorders Society. Research Grants from Parkinson’s UK, Cure Parkinson’s Trust, PSP Association, Medical Research Council, Michael J Fox Foundation. H.W.M. is a co-applicant on a patent application related to C9ORF72—Method for diagnosing a neurodegenerative disease (PCT/GB2012/052140). Z.G. Or received consultancy fees from Lysosomal Therapeutics Inc. (LTI), Idorsia, Prevail Therapeutics, Inceptions Sciences (now Ventus), Ono Therapeutics, Bial Biotech, Bial, Handl Therapeutics, UCB, Capsida, Denali Lighthouse, Guidepoint and Deerfield. E.R. was supported by Société Française de Médecine esthétique and Enjoysharing for his work on Parkinson disease. Jean-Christophe Corvol has served in advisory boards for Alzprotect, Bayer, Biogen, Denali, Ferrer, Idorsia, Prevail Therapeutic, Servier, Theranexus, UCB; and received grants from Sanofi. Kailash P. Bhatia has received grant support from Wellcome/MRC, NIHR, Parkinson’s UK and EU Horizon 2020. He receives royalties from the publication of the Oxford Specialist Handbook Parkinson’s Disease and Other Movement Disorders (Oxford University Press, 2008), of Marsden’s Book of Movement Disorders (Oxford University Press, 2012), and of Case Studies in Movement Disorders—Common and uncommon presentations (Cambridge University Press, 2017). He has received honoraria/personal compensation for participating as consultant/scientific board member from Ipsen, Allergan, Merz and honoraria for speaking at meetings and from Allergan, Ipsen, Merz, Sun Pharma, Teva, UCB Pharmaceuticals and from the American Academy of Neurology and the International Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Society. H.H. is grateful for the essential support from patients and families and for grateful funding from The Wellcome Trust, The MRC, The MSA Trust, The National Institute for Health Research University College London Hospitals Biomedical Research Centre, The Michael J Fox Foundation (MJFF), BBSRC, The Fidelity Trust, Rosetrees Trust, Ataxia UK, Brain Research UK, Sparks GOSH Charity, Alzheimer’s Research UK (ARUK) and CureDRPLA. D.N. has a research collaboration with Spark Therapeutics for which he receives research funding support. M.B. received honoraria from Ipsen Pharma. L.-L.M. has received research support grants from INSERM, JNLF, The L’Oreal Foundation, the French Parkinson Association, Fondation of France, Paris Brain Institute BBT and Neurocatalyst calls; speech honoraria from CSL, Sanofi-Genzyme, Lundbeck, Teva; consultant for Accure therapeutics, Sanofi and received travel funding from the Movement Disorders Society, ANAINF, Merck, Merz, Medtronic, Teva and AbbVie, outside the submitted work. All other authors declare no financial or non-financial competing interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

