Diagnostic value of IgG antibody and stool antigen tests for chronic Helicobacter pylori infections in Ibb Governorate, Yemen
- PMID: 38553516
- PMCID: PMC10980813
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-58165-w
Diagnostic value of IgG antibody and stool antigen tests for chronic Helicobacter pylori infections in Ibb Governorate, Yemen
Abstract
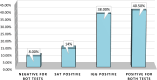
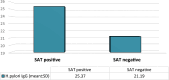
The stool antigen test (SAT) and the serum Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) IgG antibody assays exhibit significant utility in the clinical diagnosis of H. pylori infection and in distinguishing between acute and chronic infections. The main objective of the current study was to identify the diagnostic value of serum H. pylori IgG antibody and SAT in the detection of H. pylori infections among chronic H. pylori-infected patients residing in Ibb Governorate, Yemen. 200 patients with H. pylori infection, confirmed through positive results in the serum immunochromatographic antibody test, were selected for H. pylori infection confirmation using serum H. pylori IgG antibodies and SAT across diverse hospitals, gastroenterology, and Hepatology clinics in Ibb Governorate. After the selection of patients, blood and stool specimens were obtained from all participants and underwent analysis via the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). The prevalence of H. pylori infection demonstrated variability based on the confirmatory tests, with rates of 54% for SAT and 78.5% for serum H. pylori IgG antibody, contrasting with a 100% prevalence observed in the screening serum immunochromatographic antibody test. Clinically, the study categorized H. pylori infections into four stages, whereby a significant proportion of patients (40.5%) exhibited positivity for both serum H. pylori IgG antibody and SAT, indicative of active chronic infections. The majority of positive cases only manifested serum H. pylori IgG antibody presence (chronic infections) at 38%, whereas 13.5% exclusively tested positive for SAT, corresponding to acute infections. Moreover, 88% of patients did not have either serum H. pylori IgG antibody or SAT (absence of infections) during confirmatory tests. Noteworthy is the study's approach employing multiple tests for H. pylori infection detection, focusing predominantly on chronic infections-prevailing types caused by H. pylori. The results revealed a significant association between serum levels of H. pylori IgG antibody and SAT results with the presence of diverse gastrointestinal symptoms among patients, which increased with long H. pylori infection durations.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gunaid AA, Hassan NA, Murray-Lyon I. Prevalence and risk factors for Helicobacter pylori infection among Yemeni dyspeptic patients. Saudi Med. J. 2003;24(5):512–517. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials