Heterologous cAd3-Ebola and MVA-EbolaZ vaccines are safe and immunogenic in US and Uganda phase 1/1b trials
- PMID: 38553525
- PMCID: PMC10980745
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-024-00833-z
Heterologous cAd3-Ebola and MVA-EbolaZ vaccines are safe and immunogenic in US and Uganda phase 1/1b trials
Abstract
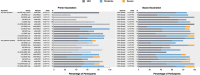
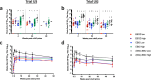
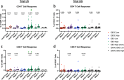
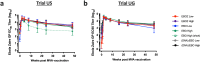
Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a filoviral infection caused by virus species of the Ebolavirus genus including Zaire ebolavirus (EBOV) and Sudan ebolavirus (SUDV). We investigated the safety and immunogenicity of a heterologous prime-boost regimen involving a chimpanzee adenovirus 3 vectored Ebola vaccine [either monovalent (cAd3-EBOZ) or bivalent (cAd3-EBO)] prime followed by a recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara EBOV vaccine (MVA-EbolaZ) boost in two phase 1/1b randomized open-label clinical trials in healthy adults in the United States (US) and Uganda (UG). Trial US (NCT02408913) enrolled 140 participants, including 26 EVD vaccine-naïve and 114 cAd3-Ebola-experienced participants (April-November 2015). Trial UG (NCT02354404) enrolled 90 participants, including 60 EVD vaccine-naïve and 30 DNA Ebola vaccine-experienced participants (February-April 2015). All tested vaccines and regimens were safe and well tolerated with no serious adverse events reported related to study products. Solicited local and systemic reactogenicity was mostly mild to moderate in severity. The heterologous prime-boost regimen was immunogenic, including induction of durable antibody responses which peaked as early as two weeks and persisted up to one year after each vaccination. Different prime-boost intervals impacted the magnitude of humoral and cellular immune responses. The results from these studies demonstrate promising implications for use of these vaccines in both prophylactic and outbreak settings.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
N.J.S. is listed on patents involving cAd3-vectored vaccines. N.R. is a paid consultant for ICON and EMMES as a safety consultant for clinical trials, and serves on the advisory boards for GSK, Sanofi, Seqirus and Moderna. Emory receives funds for N.R. to conduct research from Sanofi, Lilly, Merck, Quidel and Pfizer. M.J.M. reported potential competing interests: laboratory research and clinical trials contract funding for vaccines or MAB with Lilly, Pfizer, and Sanofi; personal fees for Scientific Advisory Board service from Merck, Meissa Vaccines, Inc. and Pfizer. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO to identify pathogens that could cause future outbreaks and pandemics. Last Update November 21, 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/21-11-2022-who-to-identify-pathogens-that-... (accessed 02/13/2023).
-
- World Health Organization. Ebola Virus Disease. February 23, 2021. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ebola-virus-disease (accessed 08/24/2021).
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ebola Disease Distribution Map: Cases of Ebola Disease in Africa Since 1976. March 24, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/history/distribution-map.html (accessed 02/21/2023).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

