Cyclophilin A supports translation of intrinsically disordered proteins and affects haematopoietic stem cell ageing
- PMID: 38553595
- PMCID: PMC11021199
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-024-01387-x
Cyclophilin A supports translation of intrinsically disordered proteins and affects haematopoietic stem cell ageing
Abstract
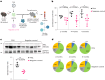
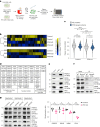
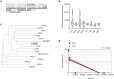
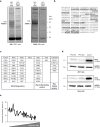
Loss of protein function is a driving force of ageing. We have identified peptidyl-prolyl isomerase A (PPIA or cyclophilin A) as a dominant chaperone in haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Depletion of PPIA accelerates stem cell ageing. We found that proteins with intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) are frequent PPIA substrates. IDRs facilitate interactions with other proteins or nucleic acids and can trigger liquid-liquid phase separation. Over 20% of PPIA substrates are involved in the formation of supramolecular membrane-less organelles. PPIA affects regulators of stress granules (PABPC1), P-bodies (DDX6) and nucleoli (NPM1) to promote phase separation and increase cellular stress resistance. Haematopoietic stem cell ageing is associated with a post-transcriptional decrease in PPIA expression and reduced translation of IDR-rich proteins. Here we link the chaperone PPIA to the synthesis of intrinsically disordered proteins, which indicates that impaired protein interaction networks and macromolecular condensation may be potential determinants of haematopoietic stem cell ageing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

