Paradoxical cancer cell proliferation after FGFR inhibition through decreased p21 signaling in FGFR1-amplified breast cancer cells
- PMID: 38553760
- PMCID: PMC10979625
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-024-01808-7
Paradoxical cancer cell proliferation after FGFR inhibition through decreased p21 signaling in FGFR1-amplified breast cancer cells
Abstract
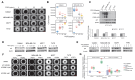
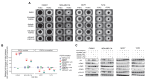
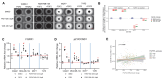
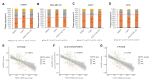
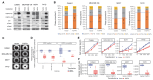
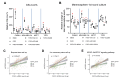
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) control various cellular functions through fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) activation, including proliferation, differentiation, migration, and survival. FGFR amplification in ER + breast cancer patients correlate with poor prognosis, and FGFR inhibitors are currently being tested in clinical trials. By comparing three-dimensional spheroid growth of ER + breast cancer cells with and without FGFR1 amplification, our research discovered that FGF2 treatment can paradoxically decrease proliferation in cells with FGFR1 amplification or overexpression. In contrast, FGF2 treatment in cells without FGFR1 amplification promotes classical FGFR proliferative signaling through the MAPK cascade. The growth inhibitory effect of FGF2 in FGFR1 amplified cells aligned with an increase in p21, a cell cycle inhibitor that hinders the G1 to S phase transition in the cell cycle. Additionally, FGF2 addition in FGFR1 amplified cells activated JAK-STAT signaling and promoted a stem cell-like state. FGF2-induced paradoxical effects were reversed by inhibiting p21 or the JAK-STAT pathway and with pan-FGFR inhibitors. Analysis of patient ER + breast tumor transcriptomes from the TCGA and METABRIC datasets demonstrated a strong positive association between expression of FGF2 and stemness signatures, which was further enhanced in tumors with high FGFR1 expression. Overall, our findings reveal a divergence in FGFR signaling, transitioning from a proliferative to stemness state driven by activation of JAK-STAT signaling and modulation of p21 levels. Activation of these divergent signaling pathways in FGFR amplified cancer cells and paradoxical growth effects highlight a challenge in the use of FGFR inhibitors in cancer treatment.
Keywords: FGF2; FGFR1; JAK-STAT; Stemness; p21.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Apelin promotes proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in bladder cancer by activating the FGF2/FGFR1 pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025 Jun 20;45(6):1289-1296. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.18. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40579142 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Analysis of Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 Impact and Mechanism on Broncho-Pulmonary Dysplasia.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2025;186(8):769-783. doi: 10.1159/000543105. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39694023
-
Progesterone Receptor Signaling Promotes Cancer Associated Fibroblast Mediated Tumorigenicity in ER+ Breast Cancer.Endocrinology. 2024 Jul 26;165(9):bqae092. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae092. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 39041201 Free PMC article.
-
LHRH agonists for adjuvant therapy of early breast cancer in premenopausal women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Oct 7;2009(4):CD004562. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004562.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 19821328 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
Cited by
-
E3 ligase MIB1 regulates STAT1/P21 signaling via regulation of FGFR1 in colorectal cancer.Genes Genomics. 2025 Jun;47(6):663-670. doi: 10.1007/s13258-025-01629-8. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Genes Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40063182
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

