RNA polymerase SI3 domain modulates global transcriptional pausing and pause-site fluctuations
- PMID: 38554114
- PMCID: PMC11077087
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae209
RNA polymerase SI3 domain modulates global transcriptional pausing and pause-site fluctuations
Abstract
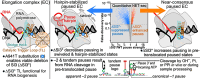
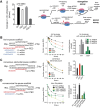
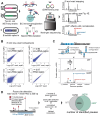
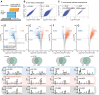
Transcriptional pausing aids gene regulation by cellular RNA polymerases (RNAPs). A surface-exposed domain inserted into the catalytic trigger loop (TL) of Escherichia coli RNAP, called SI3, modulates pausing and is essential for growth. Here we describe a viable E. coli strain lacking SI3 enabled by a suppressor TL substitution (β'Ala941→Thr; ΔSI3*). ΔSI3* increased transcription rate in vitro relative to ΔSI3, possibly explaining its viability, but retained both positive and negative effects of ΔSI3 on pausing. ΔSI3* inhibited pauses stabilized by nascent RNA structures (pause hairpins; PHs) but enhanced other pauses. Using NET-seq, we found that ΔSI3*-enhanced pauses resemble the consensus elemental pause sequence whereas sequences at ΔSI3*-suppressed pauses, which exhibited greater association with PHs, were more divergent. ΔSI3*-suppressed pauses also were associated with apparent pausing one nucleotide upstream from the consensus sequence, often generating tandem pause sites. These '-2 pauses' were stimulated by pyrophosphate in vitro and by addition of apyrase to degrade residual NTPs during NET-seq sample processing. We propose that some pauses are readily reversible by pyrophosphorolysis or single-nucleotide cleavage. Our results document multiple ways that SI3 modulates pausing in vivo and may explain discrepancies in consensus pause sequences in some NET-seq studies.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Transcriptome-Wide Effects of NusA on RNA Polymerase Pausing in Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2022 May 17;204(5):e0053421. doi: 10.1128/jb.00534-21. Epub 2022 Mar 8. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 35258320 Free PMC article.
-
Obligate movements of an active site-linked surface domain control RNA polymerase elongation and pausing via a Phe pocket anchor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 7;118(36):e2101805118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2101805118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34470825 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Polymerase Accommodates a Pause RNA Hairpin by Global Conformational Rearrangements that Prolong Pausing.Mol Cell. 2018 Mar 1;69(5):802-815.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.01.018. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29499135 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Pausing as a Mediator of Bacterial Gene Regulation.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2021 Oct 8;75:291-314. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-051721-043826. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34348029 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Transcriptional Pausing in Bacteria.J Mol Biol. 2019 Sep 20;431(20):4007-4029. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.07.017. Epub 2019 Jul 13. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31310765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bacteroides expand the functional versatility of a conserved transcription factor and transcribed DNA to program capsule diversity.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 30;15(1):10862. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55215-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39738018 Free PMC article.
-
Nanopore tweezers show fractional-nucleotide translocation in sequence-dependent pausing by RNA polymerase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 16;121(29):e2321017121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2321017121. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38990947 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical characterization of Mycobacterial RNA polymerases.J Bacteriol. 2024 Oct 24;206(10):e0025624. doi: 10.1128/jb.00256-24. Epub 2024 Sep 24. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 39315796 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Polymerase II Activity Control of Gene Expression and Involvement in Disease.J Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 1;437(1):168770. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168770. Epub 2024 Aug 28. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39214283 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Landick R. Transcriptional pausing as a mediator of bacterial gene regulation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2021; 75:291–314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

