23-Hydroxybetulinic acid attenuates 5-fluorouracil resistance of colorectal cancer by modulating M2 macrophage polarization via STAT6 signaling
- PMID: 38554148
- PMCID: PMC10981607
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-024-03662-0
23-Hydroxybetulinic acid attenuates 5-fluorouracil resistance of colorectal cancer by modulating M2 macrophage polarization via STAT6 signaling
Abstract
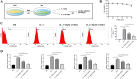
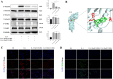
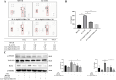
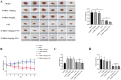
Macrophage polarization is closely associated with the inflammatory processes involved in the development and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer (CRC). M2 macrophages, the predominant subtype of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in a wide variety of malignancies, have been demonstrated to promote the resistance of CRC to multiple chemotherapeutic drugs, such as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). In our study, we investigated the potential of 23-Hydroxybetulinic Acid (23-HBA), a significant active component of Pulsatilla chinensis (P. chinensis), to inhibit the polarization of M2 macrophages induced by IL-4. Our results showed that 23-HBA reduced the expression of M2 specific marker CD206, while downregulating the mRNA levels of M2 related genes (CD206, Arg1, IL-10, and CCL2). Additionally, 23-HBA effectively attenuated the inhibitory effects of the conditioned medium from M2 macrophages on apoptosis in colorectal cancer SW480 cells. Mechanistically, 23-HBA prevented the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of the STAT6 protein, resulting in the inhibition of IL-10 release in M2 macrophages. Moreover, it interfered with the activation of the IL-10/STAT3/Bcl-2 signaling pathway in SW480 cells, ultimately reducing M2 macrophage-induced resistance to 5-FU. Importantly, depleting STAT6 expression in macrophages abolished the suppressive effect of 23-HBA on M2 macrophage polarization, while also eliminating its ability to decrease M2 macrophage-induced 5-FU resistance in cancer cells. Furthermore, 23-HBA significantly diminished the proportion of M2 macrophages in the tumor tissues of colorectal cancer mice, simultaneously enhancing the anti-cancer efficacy of 5-FU. The findings presented in this study highlight the capacity of 23-HBA to inhibit M2 macrophage polarization, a process that contributes to reduced 5-FU resistance in colorectal cancer.
Keywords: 23-Hydroxybetulinic acid; 5-fluorouracil; Chemoresistance; Colorectal cancer; Macrophage polarization; STAT6.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

