Lipid droplets-related Perilipin-3: potential immune checkpoint and oncogene in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38554152
- PMCID: PMC10981595
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-024-03659-9
Lipid droplets-related Perilipin-3: potential immune checkpoint and oncogene in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Lipid droplets (LDs) as major lipid storage organelles are recently reported to be innate immune hubs. Perilipin-3 (PLIN3) is indispensable for the formation and accumulation of LDs. Since cancer patients show dysregulated lipid metabolism, we aimed to elaborate the role of LDs-related PLIN3 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
Methods: PLIN3 expression patterns (n = 87), its immune-related landscape (n = 74) and association with B7-H2 (n = 51) were assessed by immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry. Real-time PCR, Western blot, Oil Red O assay, immunofluorescence, migration assay, spheroid-forming assay and flow cytometry were performed for function analysis.
Results: Spotted LDs-like PLIN3 staining was dominantly enriched in tumor cells than other cell types. PLIN3high tumor showed high proliferation index with metastasis potential, accompanied with less CD3+CD8+ T cells in peripheral blood and in situ tissue, conferring immunosuppressive microenvironment and shorter postoperative survival. Consistently, PLIN3 knockdown in tumor cells not only reduced LD deposits and tumor migration, but benefited for CD8+ T cells activation in co-culture system with decreased B7-H2. An OSCC subpopulation harbored PLIN3highB7-H2high tumor showed more T cells exhaustion, rendering higher risk of cancer-related death (95% CI 1.285-6.851).
Conclusions: LDs marker PLIN3 may be a novel immunotherapeutic target in OSCC.
Keywords: B7-H2; Lipid droplets; OSCC; PD-L1; Perilipin-3.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

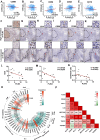


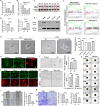
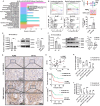

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

