Structure-based inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase with 2-Aryl-6-carboxamide benzoxazole derivatives: synthesis, enzymatic assay, and in silico studies
- PMID: 38554169
- PMCID: PMC11785640
- DOI: 10.1007/s11030-024-10828-6
Structure-based inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase with 2-Aryl-6-carboxamide benzoxazole derivatives: synthesis, enzymatic assay, and in silico studies
Abstract
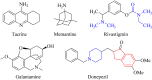
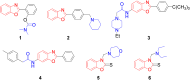
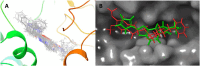
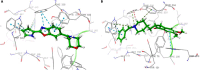
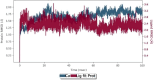
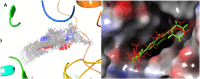
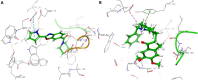
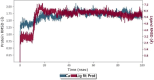
An important research topic is the discovery of multifunctional compounds targeting different disease-causing components. This research aimed to design and synthesize a series of 2-aryl-6-carboxamide benzoxazole derivatives that inhibit cholinesterases on both the peripheral anionic and catalytic anionic sides. Compounds (7-48) were prepared from 4-amino-3-hydroxybenzoic acid in three steps. The Ellman test, molecular docking with Maestro, and molecular dynamics simulation studies with Desmond were done (Schrodinger, 12.8.117). Compound 36, the most potent compound among the 42 new compounds synthesized, had an inhibitory concentration of IC50 12.62 nM for AChE and IC50 25.45 nM for BChE (whereas donepezil was 69.3 nM and 63.0 nM, respectively). Additionally, compound 36 had docking values of - 7.29 kcal/mol for AChE and - 6.71 kcal/mol for BChE (whereas donepezil was - 6.49 kcal/mol and - 5.057 kcal/mol, respectively). Furthermore, molecular dynamics simulations revealed that compound 36 is stable in the active gorges of both AChE (average RMSD: 1.98 Å) and BChE (average RMSD: 2.2 Å) (donepezil had average RMSD: 1.65 Å and 2.7 Å, respectively). The results show that compound 36 is a potent, selective, mixed-type dual inhibitor of both acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. It does this by binding to both the catalytically active and peripheral anionic sites of cholinesterases at the same time. These findings show that target compounds may be useful for establishing the structural basis for new anti-Alzheimer agents.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase; Benzoxazole; Butyrylcholinesterase; Enzyme inhibition; Molecular docking and dynamic simulation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

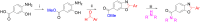

References
-
- Patterson C, World Alzheimer Report https://apo.org.au/node/260056 (accessed 12 October 2022). 4., Giacobini E (2018) (2003) Cholinesterases: new roles in brain function and in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res. 10.1023/A:1022869222652 - PubMed
-
- Giacobini E (2003) Cholinesterases: new roles in brain function and in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res 28(3/4):515–522. 10.1023/A:1022869222652 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

