Clinically used broad-spectrum antibiotics compromise inflammatory monocyte-dependent antibacterial defense in the lung
- PMID: 38555356
- PMCID: PMC10981692
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47149-z
Clinically used broad-spectrum antibiotics compromise inflammatory monocyte-dependent antibacterial defense in the lung
Abstract
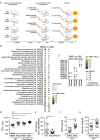
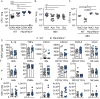
Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) is associated with high mortality and costs, and frequently caused by multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. Although prior antimicrobial therapy is a major risk factor for HAP, the underlying mechanism remains incompletely understood. Here, we demonstrate that antibiotic therapy in hospitalized patients is associated with decreased diversity of the gut microbiome and depletion of short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) producers. Infection experiments with mice transplanted with patient fecal material reveal that these antibiotic-induced microbiota perturbations impair pulmonary defense against MDR Klebsiella pneumoniae. This is dependent on inflammatory monocytes (IMs), whose fatty acid receptor (FFAR)2/3-controlled and phagolysosome-dependent antibacterial activity is compromized in mice transplanted with antibiotic-associated patient microbiota. Collectively, we characterize how clinically relevant antibiotics affect antimicrobial defense in the context of human microbiota, and reveal a critical impairment of IM´s antimicrobial activity. Our study provides additional arguments for the rational use of antibiotics and offers mechanistic insights for the development of novel prophylactic strategies to protect high-risk patients from HAP.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Torres, A. et al. International ERS/ESICM/ESCMID/ALAT guidelines for the management of hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia: Guidelines for the management of hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP)/ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) of the European Respiratory Society (ERS), European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM), European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) and Asociacion Latinoamericana del Torax (ALAT). Eur. Respir. J. 5010.1183/13993003.00582-2017 (2017). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- OP 86/12-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- OP 86/13-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- SFB-TR84 A5/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- SFB 1449 B02/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- SFB-TR84 A5/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

