Modified Percutaneous Endoscopic Interlaminar Discectomy through the Near-spinous Process Approach for L4/5 Disc Herniation: A Retrospective Clinical Study
- PMID: 38556483
- PMCID: PMC11062861
- DOI: 10.1111/os.14031
Modified Percutaneous Endoscopic Interlaminar Discectomy through the Near-spinous Process Approach for L4/5 Disc Herniation: A Retrospective Clinical Study
Abstract
Objective: Compared with traditional open surgery, percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy (PELD) has the advantages of less trauma, faster recovery, and less postoperative pain, so it has been widely used in the field of spinal surgery. However, it still has the defect of intraoperative fluoroscopy occurrences, complications, and even the risk of damage to the spinal cord and nerve. This study aims to compare the clinical efficacy of modified percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy (MPEID) with percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy (PETD) in treating L4/5 lumbar disc herniation (LDH) and to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of MPEID.
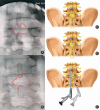
Methods: Thirty-four L4/5 LDH patients treated at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University from June 2020 to June 2021 were studied retrospectively. Seventeen underwent MPEID and seventeen PETD. Variables analyzed included demographics, operative duration, intraoperative fluoroscopy occurrences, and surgical outcomes. Effectiveness was evaluated using the visual analogue scale (VAS), Oswestry disability index (ODI), and modified MacNab criteria. Lumbar Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) was used to assess radiological outcomes. A paired t-test was performed to compare intragroup pre- and postoperative clinical data, VAS, and ODI scores.
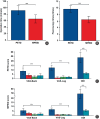
Results: The average operative time in PETD group was 91.65 ± 14.04 min, and the average operative time in MPEID group was 65.41 ± 12.61 min (p < 0.001). In PETD group, the fluoroscopy occurrences averaged 9.71 ± 1.05 times, with fluoroscopy occurrences averaging 6.47 ± 1.00 times (p < 0.001) in MPEID group. At 12 months follow-up, the clinical effect showed significant improvement in both two groups. The MPEID group showed a decrease in average VAS-back score from 5.41 ± 2.18 to 1.76 ± 1.09 (p < 0.001) and VAS-leg score from 6.53 ± 1.66 to 0.82 ± 0.64 (p < 0.001). The ODI scores decreased from 51.35 ± 10.65 to 11.71 ± 2.91 (p < 0.001). In the PETD group, the VAS-back score decreased from 4.94 ± 1.98 to 2.06 ± 1.25 (p < 0.001), VAS-leg score from 7.12 ± 1.73 to 1.12 ± 0.60 (p < 0.001), and ODI scores from 48.00 ± 11.62 to 12.24 ± 2.56 (p < 0.001). According to the modified MacNab criteria, MPEID had 15 excellent and two good results; PETD had 12 excellent and 5 good (p = 0.23). No nerve root injuries, dural tears, or significant complications were reported.
Conclusion: MPEID and PETD effectively treat L4/5 LDH, with MPEID showing shorter operative times and fewer fluoroscopies. Furthermore, the MPEID group can provide excellent clinical efficacy as the PETD group in the short term.
Keywords: L4/5 Lumbar disc herniation; Percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy; Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy; Percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy.
© 2024 The Authors. Orthopaedic Surgery published by Tianjin Hospital and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Yu H, Zhu B, Liu X. Comparison of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy and open lumbar discectomy in the treatment of adolescent lumbar disc herniation: a retrospective analysis. World Neurosurg. 2021;151:e911–e917. - PubMed
-
- Yeung AT, Tsou PM. Posterolateral endoscopic excision for lumbar disc herniation: surgical technique, outcome, and complications in 307 consecutive cases. Spine. 2002;27:722–731. - PubMed
-
- Ruetten S, Komp M, Godolias G. A new full‐endoscopic technique for the interlaminar operation of lumbar disc herniations using 6‐mm endoscopes: prospective 2‐year results of 331 patients. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2006;49:80–87. - PubMed
-
- Kapetanakis S, Gkantsinikoudis N, Charitoudis G. Implementation of percutaneous Transforaminal endoscopic discectomy in competitive elite athletes with lumbar disc herniation: original study and review of the literature. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(12):3234–3241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

