The acute phase reactant orosomucoid-2 directly promotes rheumatoid inflammation
- PMID: 38556552
- PMCID: PMC11058272
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-024-01188-0
The acute phase reactant orosomucoid-2 directly promotes rheumatoid inflammation
Abstract
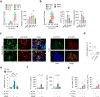
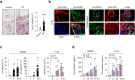
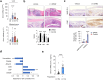
Acute phase proteins involved in chronic inflammatory diseases have not been systematically analyzed. Here, global proteome profiling of serum and urine revealed that orosomucoid-2 (ORM2), an acute phase reactant, was differentially expressed in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and showed the highest fold change. Therefore, we questioned the extent to which ORM2, which is produced mainly in the liver, actively participates in rheumatoid inflammation. Surprisingly, ORM2 expression was upregulated in the synovial fluids and synovial membranes of RA patients. The major cell types producing ORM2 were synovial macrophages and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) from RA patients. Recombinant ORM2 robustly increased IL-6, TNF-α, CXCL8 (IL-8), and CCL2 production by RA macrophages and FLSs via the NF-κB and p38 MAPK pathways. Interestingly, glycophorin C, a membrane protein for determining erythrocyte shape, was the receptor for ORM2. Intra-articular injection of ORM2 increased the severity of arthritis in mice and accelerated the infiltration of macrophages into the affected joints. Moreover, circulating ORM2 levels correlated with RA activity and radiographic progression. In conclusion, the acute phase protein ORM2 can directly increase the production of proinflammatory mediators and promote chronic arthritis in mice, suggesting that ORM2 could be a new therapeutic target for RA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibition of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase suppresses fibroblast-like synoviocytes-mediated synovial inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 May;174(9):893-908. doi: 10.1111/bph.13762. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28239846 Free PMC article.
-
C-Reactive Protein Promotes the Activation of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes From Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2020 May 20;11:958. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00958. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32508836 Free PMC article.
-
IL-26 is overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis and induces proinflammatory cytokine production and Th17 cell generation.PLoS Biol. 2012;10(9):e1001395. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001395. Epub 2012 Sep 25. PLoS Biol. 2012. PMID: 23055831 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Adiponectin in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 4;21(21):8265. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218265. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33158216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Survivin a pivotal antiapoptotic protein in rheumatoid arthritis.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Dec;234(12):21575-21587. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28784. Epub 2019 May 6. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31062383 Review.
Cited by
-
L-shaped correlation between serum alpha-1-acid glycoprotein concentration and urinary albumin creatinine ratio in females: a cross-sectional survey.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 24;16:1438695. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1438695. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40196454 Free PMC article.
-
ORM1 Mediates Ln-IgG-Induced Podocyte Damage and Autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR Signaling.Organogenesis. 2025 Dec;21(1):2519614. doi: 10.1080/15476278.2025.2519614. Epub 2025 Jun 17. Organogenesis. 2025. PMID: 40526157 Free PMC article.
-
Fibromyalgia and Inflammation: Unrevealing the Connection.Cells. 2025 Feb 13;14(4):271. doi: 10.3390/cells14040271. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39996743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synovial Fluid Markers and Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Nov 26;60(12):1945. doi: 10.3390/medicina60121945. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39768826 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

