Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of the AP2/EREBP, COX and LTP genes in Zea mays L. under drought stress
- PMID: 38556556
- PMCID: PMC10982304
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-57376-5
Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of the AP2/EREBP, COX and LTP genes in Zea mays L. under drought stress
Abstract
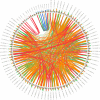
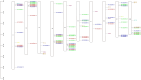
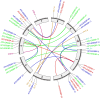
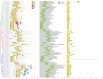
AP2 (APETALA2)/EREBP (ethylene-responsive element-binding protein), cytochrome c oxidase (COX) and nonspecific lipid transfer proteins (LTP) play important roles in the response to drought stress. This is the first study to identify the COX gene in Zea mays L. via genome-wide analysis. The qRT‒PCR results indicated that AP2/EREBP, COX and LTP were downregulated, with fold changes of 0.84, 0.53 and 0.31, respectively, after 12 h of drought stress. Genome-wide analysis identified 78 AP2/EREBP, 6 COX and 10 LTP genes in Z. mays L. Domain analysis confirmed the presence of the AP2 domain, Cyt_c_Oxidase_Vb domain and nsLTP1 in the AP2/EREBP, COX and LTP proteins, respectively. The AP2/EREBP protein family (AP2) includes five different domain types: the AP2/ERF domain, the EREBP-like factor (EREBP), the ethylene responsive factor (ERF), the dehydration responsive element binding protein (DREB) and the SHN SHINE. Synteny analysis of the AP2/EREBP, COX and LTP genes revealed collinearity orthologous relationships in O. sativa, H. vulgare and A. thaliana. AP2/EREBP genes were found on the 10 chromosomes of Z. mays L. COX genes were found on chromosomes 1, 3, 4, 5, 7 and 8. LTP genes were found on chromosomes 1, 3, 6, 8, 9 and 10. In the present study, the Ka/Ks ratios of the AP2/EREBP paralogous pairs indicated that the AP2/EREBP genes were influenced primarily by purifying selection, which indicated that the AP2/EREBP genes received strong environmental pressure during evolution. The Ka/Ks ratios of the COX-3/COX-4 paralogous pairs indicate that the COX-3/COX-4 genes were influenced primarily by Darwinian selection (driving change). For the LTP genes, the Ka/Ks ratios of the LTP-1/LTP-10, LTP-5/LTP-3 and LTP-4/LTP-8 paralogous pairs indicate that these genes were influenced primarily by purifying selection, while the Ka/Ks ratios of the LTP-2/LTP-6 paralogous pairs indicate that these genes were influenced primarily by Darwinian selection. The duplication time of the AP2/EREBP paralogous gene pairs in Z. mays L. ranged from approximately 9.364 to 100.935 Mya. The duplication time of the COX-3/COX-4 paralogous gene pair was approximately 5.217 Mya. The duplication time of the LTP paralogous gene pairs ranged from approximately 19.064 to 96.477 Mya. The major focus of research is to identify the genes that are responsible for drought stress tolerance to improve maize for drought stress tolerance. The results of the present study will improve the understanding of the functions of the AP2/EREBP, COX and LTP genes in response to drought stress.
Keywords: AP2/EREBP; COX; LTP; Drought stress; Evolutionary analysis; Genome-wide identification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expansion and stress responses of the AP2/EREBP superfamily in cotton.BMC Genomics. 2017 Jan 31;18(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3517-9. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28143399 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of maize AP2/ERF superfamily genes reveal essential roles in abiotic stress tolerance.BMC Genomics. 2022 Feb 12;23(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08345-7. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35151253 Free PMC article.
-
Wide-Range Portrayal of AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Family in Maize (Zea mays L.) Development and Stress Responses.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;14(1):194. doi: 10.3390/genes14010194. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672935 Free PMC article.
-
Advances of Apetala2/Ethylene Response Factors in Regulating Development and Stress Response in Maize.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 12;24(6):5416. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065416. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AP2/EREBP transcription factors are part of gene regulatory networks and integrate metabolic, hormonal and environmental signals in stress acclimation and retrograde signalling.Protoplasma. 2010 Sep;245(1-4):3-14. doi: 10.1007/s00709-010-0142-8. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Protoplasma. 2010. PMID: 20411284 Review.
Cited by
-
GWAS and Meta-QTL Analysis of Kernel Quality-Related Traits in Maize.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 29;13(19):2730. doi: 10.3390/plants13192730. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409600 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study and genotypic variation for the major tocopherol content in rice grain.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Oct 8;15:1426321. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1426321. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39439508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Warrick, R. A. Drought Hazard in the United States: A Research Assessment. Monograph no. NSF/RA/E-75/004, 199. (University of Colorado, Institute of Behavorial Science, 1975).
-
- Huschke RE, editor. Glossary of Meteorology. American Meteorological Society; 1959. p. 638.
-
- Rosenberg, N. J., ed. Drought in the Great Plains-Research on impacts and strategies. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Research in Great Plains Drought Management Strategies, University of Nebraska, Lincoln 225. (Water Resources Publications, 1979).
-
- Yevjevich, V., Hall, W. A. & Salas, J. D., eds. Drought research needs. In Proceedings of the Conference on Drought Research Needs 276. (Colorado State University, 1977).
-
- The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) https://www.fao.org
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

