LXRα Promotes Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Formation Through UHRF1 Epigenetic Modification of miR-26b-3p
- PMID: 38557060
- PMCID: PMC11219073
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.065202
LXRα Promotes Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Formation Through UHRF1 Epigenetic Modification of miR-26b-3p
Abstract
Background: Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a severe aortic disease without effective pharmacological approaches. The nuclear hormone receptor LXRα (liver X receptor α), encoded by the NR1H3 gene, serves as a critical transcriptional mediator linked to several vascular pathologies, but its role in AAA remains elusive.
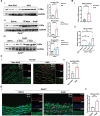
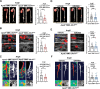
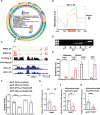
Methods: Through integrated analyses of human and murine AAA gene expression microarray data sets, we identified NR1H3 as a candidate gene regulating AAA formation. To investigate the role of LXRα in AAA formation, we used global Nr1h3-knockout and vascular smooth muscle cell-specific Nr1h3-knockout mice in 2 AAA mouse models induced with angiotensin II (1000 ng·kg·min; 28 days) or calcium chloride (CaCl2; 0.5 mol/L; 42 days).
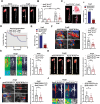
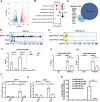
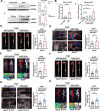
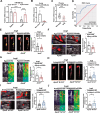
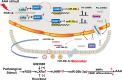
Results: Upregulated LXRα was observed in the aortas of patients with AAA and in angiotensin II- or CaCl2-treated mice. Global or vascular smooth muscle cell-specific Nr1h3 knockout inhibited AAA formation in 2 mouse models. Loss of LXRα function prevented extracellular matrix degeneration, inflammation, and vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching. Uhrf1, an epigenetic master regulator, was identified as a direct target gene of LXRα by integrated analysis of transcriptome sequencing and chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing. Susceptibility to AAA development was consistently enhanced by UHRF1 (ubiquitin-like containing PHD and RING finger domains 1) in both angiotensin II- and CaCl2-induced mouse models. We then determined the CpG methylation status and promoter accessibility of UHRF1-mediated genes using CUT&Tag (cleavage under targets and tagmentation), RRBS (reduced representation bisulfite sequencing), and ATAC-seq (assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with sequencing) in vascular smooth muscle cells, which revealed that the recruitment of UHRF1 to the promoter of miR-26b led to DNA hypermethylation accompanied by relatively closed chromatin states, and caused downregulation of miR-26b expression in AAA. Regarding clinical significance, we found that underexpression of miR-26b-3p correlated with high risk in patients with AAA. Maintaining miR-26b-3p expression prevented AAA progression and alleviated the overall pathological process.
Conclusions: Our study reveals a pivotal role of the LXRα/UHRF1/miR-26b-3p axis in AAA and provides potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for AAA.
Keywords: aortic aneurysm, abdominal; biomarkers; myocytes, smooth muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
A New Molecular Axis to Tackle the Development of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.Circulation. 2024 Jul 2;150(1):47-48. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.069916. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Circulation. 2024. PMID: 38950116 No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

