IBPGNET: lung adenocarcinoma recurrence prediction based on neural network interpretability
- PMID: 38557672
- PMCID: PMC10982951
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbae080
IBPGNET: lung adenocarcinoma recurrence prediction based on neural network interpretability
Abstract
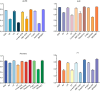
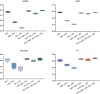
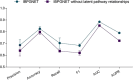
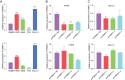
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common histologic subtype of lung cancer. Early-stage patients have a 30-50% probability of metastatic recurrence after surgical treatment. Here, we propose a new computational framework, Interpretable Biological Pathway Graph Neural Networks (IBPGNET), based on pathway hierarchy relationships to predict LUAD recurrence and explore the internal regulatory mechanisms of LUAD. IBPGNET can integrate different omics data efficiently and provide global interpretability. In addition, our experimental results show that IBPGNET outperforms other classification methods in 5-fold cross-validation. IBPGNET identified PSMC1 and PSMD11 as genes associated with LUAD recurrence, and their expression levels were significantly higher in LUAD cells than in normal cells. The knockdown of PSMC1 and PSMD11 in LUAD cells increased their sensitivity to afatinib and decreased cell migration, invasion and proliferation. In addition, the cells showed significantly lower EGFR expression, indicating that PSMC1 and PSMD11 may mediate therapeutic sensitivity through EGFR expression.
Keywords: PSMC1 and PSMD11; lung adenocarcinoma; multi-omics data; neural network interpretability; recurrence prediction.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, et al. NCCN guidelines® insights: non-small cell lung cancer, version 2.2023. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2023;21:340–50. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 2022;72:7–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

