Systematic review on effects of experimental orthodontic tooth displacement on brain activation assessed by fMRI
- PMID: 38558512
- PMCID: PMC10982672
- DOI: 10.1002/cre2.879
Systematic review on effects of experimental orthodontic tooth displacement on brain activation assessed by fMRI
Abstract
Background: Orthodontic treatment is often accompanied by discomfort and pain in patients, which are believed to be a result of orthodontic tooth displacement caused by the mechanical forces exerted by the orthodontic appliances on the periodontal tissues. These lead to change blood oxygen level dependent response in related brain regions.
Objective: This systematic review aims to assess the impact of experimental orthodontic tooth displacement on alterations in central nervous system activation assessed by tasked based and resting state fMRI.
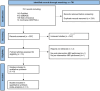
Materials and methods: A literature search was conducted using online databases, following PRISMA guidelines and the PICO framework. Selected studies utilized magnetic resonance imaging to examine the brain activity changes in healthy participants after the insertion of orthodontic appliances.
Results: The initial database screening resulted in 791 studies. Of these, 234 were duplicates and 547 were deemed irrelevant considering the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Of the ten remaining potential relevant studies, two were excluded during full-text screening. Eight prospective articles were eligible for further analysis. The included studies provided evidence of the intricate interplay between orthodontic treatment, pain perception, and brain function. All of the participants in the included studies employed orthodontic separators in short-term experiments to induce tooth displacement during the early stage of orthodontic treatment. Alterations in brain activation were observed in brain regions, functional connectivity and brain networks, predominantly affecting regions implicated in nociception (thalamus, insula), emotion (insula, frontal areas), and cognition (frontal areas, cerebellum, default mode network).
Conclusions: The results suggest that orthodontic treatment influences beyond the pain matrix and affects other brain regions including the limbic system. Furthermore, understanding the orthodontically induced brain activation can aid in development of targeted pain management strategies that do not adversely affect orthodontic tooth movement. Due to the moderate to serious risk of bias and the heterogeneity among the included studies, further clinical trials on this subject are recommended.
Keywords: brain activity; magnetic resonance imaging; orthodontic tooth movement; orthodontic treatment.
© 2024 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have stated explicitly that there are no conflicts of interest in connection with this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-surgical adjunctive interventions for accelerating tooth movement in patients undergoing orthodontic treatment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 20;6(6):CD010887. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010887.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37339352 Free PMC article.
-
Non-surgical adjunctive interventions for accelerating tooth movement in patients undergoing fixed orthodontic treatment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 18;2015(11):CD010887. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010887.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 20;6:CD010887. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010887.pub3. PMID: 26576758 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Initial arch wires used in orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 31;7(7):CD007859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007859.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Feb 06;2:CD007859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007859.pub5. PMID: 30064155 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Initial arch wires for tooth alignment during orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Apr 30;2013(4):CD007859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007859.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 31;7:CD007859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007859.pub4. PMID: 23633347 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Orthodontic treatment for distalising upper first molars in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Oct 23;2013(10):CD008375. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008375.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24155018 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adjunctive therapies in orthodontics: a scoping systematic review.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Apr 18;25(1):590. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05874-x. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40251484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggleton, J. P. , Dalgleish, P. W. , Boller, F. , & Grafman, J. (1995). The limbic system: an introduction. Handbook of Neuropsychology, 2(no. 2), 99–120.
-
- Ariji, Y. , Kondo, H. , Miyazawa, K. , Sakuma, S. , Tabuchi, M. , Kise, Y. , Nakayama, M. , Koyama, S. , Togari, A. , Goto, S. , & Ariji, E. (2019). Study on regional activities in the human brain caused by low‐level clenching and tooth separation: Investigation with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Oral Science International, 16, 87–94.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical