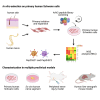
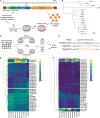
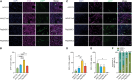
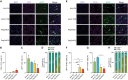
Novel AAV variants with improved tropism for human Schwann cells
- PMID: 38558569
- PMCID: PMC10978538
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101234
Novel AAV variants with improved tropism for human Schwann cells
Abstract
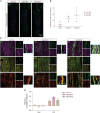
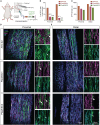
Gene therapies and associated technologies are transforming biomedical research and enabling novel therapeutic options for patients living with debilitating and incurable genetic disorders. The vector system based on recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors (AAVs) has shown great promise in recent clinical trials for genetic diseases of multiple organs, such as the liver and the nervous system. Despite recent successes toward the development of novel bioengineered AAV variants for improved transduction of primary human tissues and cells, vectors that can efficiently transduce human Schwann cells (hSCs) have yet to be identified. Here, we report the application of the functional transduction-RNA selection method in primary hSCs for the development of AAV variants for specific and efficient transgene delivery to hSCs. The two identified capsid variants, Pep2hSC1 and Pep2hSC2, show conserved potency for delivery across various in vitro, in vivo, and ex vivo models of hSCs. These novel AAV capsids will serve as valuable research tools, forming the basis for therapeutic solutions for both SC-related disorders or peripheral nervous system injury.
Keywords: AAV; Schwann cells; adeno-associated vector; directed evolution; gene therapy; vector engineering.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
M.D., J.M., M.C.-C., A.W., S.L.G., I.E.A., and L.L. are inventors on patent applications filed by Children’s Medical Research Institute related to AAV capsid sequences, in vivo function of novel AAV variants and AAV selection platforms. L.L. is a co-founder and scientific advisor of LogicBio Therapeutics. L.L. and I.A.E. are co-founders of Exigen Biotherapeutics. L.L. and I.E.A. have consulted on broad technologies addressed in this paper. L.L. and I.A.E. have stock and/or equity in companies with technology broadly related to this paper.
Figures