Efficacy of Liposuction in the Treatment of Lipedema: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38558609
- PMCID: PMC10981502
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.55260
Efficacy of Liposuction in the Treatment of Lipedema: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
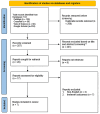
Lipedema, a chronic and painful disorder primarily affecting women without a definitive cure, has traditionally been managed with conservative therapy, notably complete decongestive therapy, across many countries. Recently, liposuction has been explored as a potential surgical treatment, prompting this study to evaluate its effectiveness as possibly the first-line therapy for lipedema. Through extensive literature searches in databases such as CrossRef, Web of Science, PubMed, and Google Scholar up to December 2023, and using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for quality assessment, the study selected seven studies for inclusion. Results showed significant post-operative improvements in spontaneous pain, edema, bruising, mobility, and quality of life among lipedema patients undergoing liposuction. However, over half of the patients still required conservative therapy after surgery. Despite these promising results, the study suggests caution due to lipedema's complexity, significant reliance on self-reported data, and limitations of the studies reviewed. Thus, while liposuction may offer symptomatic relief, it should be considered an adjunct, experimental therapy rather than a definitive cure, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive approach to care.
Keywords: large-volume liposuction; lipedema; liposuction; liposuction complication; meta-analysis.
Copyright © 2024, Amato et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Safety and Effectiveness of Liposuction Modalities in Managing Lipedema: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Arch Plast Surg. 2024 Aug 6;51(5):510-526. doi: 10.1055/a-2334-9260. eCollection 2024 Sep. Arch Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39345998 Free PMC article.
-
Liposuction for the Treatment of Lipedema: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines [Internet].Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2019 Jun 7. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2019 Jun 7. PMID: 31479212 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Improvements in patients with lipedema 4, 8 and 12 years after liposuction.Phlebology. 2021 Mar;36(2):152-159. doi: 10.1177/0268355520949775. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Phlebology. 2021. PMID: 32847472
-
A randomised controlled multicentre investigator-blinded clinical trial comparing efficacy and safety of surgery versus complex physical decongestive therapy for lipedema (LIPLEG).Trials. 2021 Oct 30;22(1):758. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05727-2. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34717741 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Liposuction as a Treatment for Lipedema: A Scoping Review.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024 Jul 2;12(7):e5952. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005952. eCollection 2024 Jul. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024. PMID: 38957726 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lipedema: Complications in High-Volume Liposuction Are Linked to Preoperative Anemia.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 19;13(24):7779. doi: 10.3390/jcm13247779. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39768702 Free PMC article.
-
Global Analysis and Latest Research Hot Spots of Lipoedema/Lipodystrophy Investigation and Management: A Bibliometric Analysis and Visualized Review.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Jul;49(13):3736-3749. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-04855-3. Epub 2025 Apr 28. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40295372 Review.
-
The Efficacy of Ketogenic Diets (Low Carbohydrate; High Fat) as a Potential Nutritional Intervention for Lipedema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 27;16(19):3276. doi: 10.3390/nu16193276. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39408242 Free PMC article.
-
Lipedema: A Disease Triggered by M2 Polarized Macrophages?Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 23;13(3):561. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030561. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149538 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lipedema: an overview of its clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of the disproportional fatty deposition syndrome - systematic review. Forner-Cordero I, Szolnoky G, Forner-Cordero A, Kemény L. Clin Obes. 2012;2:86–95. - PubMed
-
- Liposuction for the treatment of lipedema: a review of clinical effectiveness and guidelines. Peprah K, MacDougall D. https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk545818?report=printable&client=bot&... Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. 2019 - PubMed
-
- Lipedema prevalence and risk factors in Brazil. Amato AC, Amato FC, Amato JL, Benitti DA. https://www.scielo.br/j/jvb/a/Q9yR3XdzXVbrsB37KQD3mfg/?lang=en# J Vasc Bras. 2022;21:0. - PMC - PubMed
-
- First Dutch guidelines on lipedema using the international classification of functioning, disability and health. Halk AB, Damstra RJ. Phlebology. 2017;32:152–159. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
