Effectiveness of Conventional Periodontal Treatment With Tetracycline Fiber Versus Minocycline Gel Application Subgingivally in Periodontitis Patients
- PMID: 38558744
- PMCID: PMC10980540
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.55167
Effectiveness of Conventional Periodontal Treatment With Tetracycline Fiber Versus Minocycline Gel Application Subgingivally in Periodontitis Patients
Abstract
Background: Locally delivered antibiotics are adjunctive therapies for the selective removal or inhibition of pathogenic microbes in combination with scaling and root planing (SRP) for the management of periodontitis.
Objective: The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of tetracycline fibers against minocycline gel when used as local drug delivery in conjunction with SRP for treating periodontitis.
Methods and materials: This is a pilot randomized open single, blinded trial study comparing three treatment modalities: SRP with topical tetracycline fibers (SRP+T), SRP with topical minocycline HCL 2% gel (SRP+M), and SRP only as a control group. Probing pocket depth (PPD), clinical attachment loss (CAL), and bleeding on probing (BOP) percentages were recorded at baseline, one month, and at the end of three months. The data were subjected to analysis using IBM Corp. Released 2019. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 26.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp. Repeated measures ANOVA was used to compare the clinical outcomes between the three treatment groups, accounting for the repeated measurements at baseline, one month, and three months. A p-value less than 0.05 at a 95% confidence interval was deemed statistically significant.
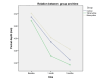
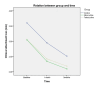
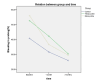
Results: There were statistically significant changes within the groups in all the clinical parameters, including pocket depth, clinical attachment loss, and bleeding on probing score, at different time intervals, with the greatest mean pocket depth changes seen in the tetracycline group after one month (mean changes = 1.4 mm, P < 0.001) and over three months (mean changes = 1.79 mm, p < 0.001). For clinical attachment loss, after one month, the highest improvement in clinical level was seen in the minocycline group (mean changes = 0.7mm, p < 0.05), and the overall improvement was seen in the control group (mean changes = 1.1mm, p < 0.05). The minocycline group showed greater mean changes in bleeding on probing percentage, with the greatest changes after one month (mean changes = 19.34%, p < 0.001) and over three months (mean changes = 26.42%, p <0.001). However, there was no significant difference between the groups.
Conclusion: Locally delivered tetracycline and minocycline gel are effective as adjuncts to SRP and may improve the healing outcome in the management of periodontitis.
Keywords: local antibiotics; minocycline; non-surgical periodontal therapy; periodontitis; tetracycline.
Copyright © 2024, Zainuddin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Subgingival pathogens in chronic periodontitis patients affected by type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective case-control study. Montevecchi M, Valeriani L, Gatto MR, D'Alessandro G, Piana G. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8718332/ J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2021;51:409–421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clinical evaluation of diode (980 nm) laser-assisted nonsurgical periodontal pocket therapy: a randomized comparative clinical trial and bacteriological study. Nammour S, El Mobadder M, Maalouf E, et al. https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/abs/10.1089/photob.2020.4818. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2021;39:10–22. - PubMed
-
- The ever-changing landscape in modern dentistry therapeutics-Enhancing the emptying quiver of the periodontist. Diakoumopoulou D, Magana M, Karoussis IK, Nikolaou C, Chatzipanagiotou S, Ioannidis A. http://chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://www.c... Heliyon. 2021;7 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nonsurgical periodontal therapy with/without 980 nm diode laser in patients after myocardial infarction: a randomized clinical trial. Samulak R, Suwała M, Dembowska E. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10103-020-03136-6. Lasers Med Sci. 2021;36:1003–1014. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tetracycline antibiotics and resistance. Grossman TH. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4817740/ Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016;6:0. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
