Modulation of expression of Connexins 37, 40 and 43 in endothelial cells in culture
- PMID: 38558785
- PMCID: PMC10978589
- DOI: 10.3389/fnetp.2024.1199198
Modulation of expression of Connexins 37, 40 and 43 in endothelial cells in culture
Abstract
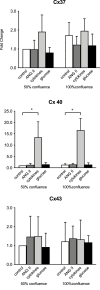
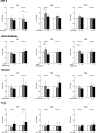
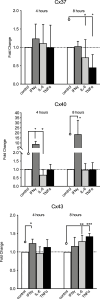
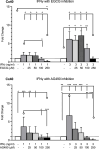
Connexin (Cx) 37, 40, and 43 are implicated in vascular function, specifically in the electrical coupling of endothelial cells and vascular smooth-muscle cells. In the present study, we investigated whether factors implicated in vascular dysfunction can modulate the gene expression of Cx37, Cx40, and Cx43 and whether this is associated with changes in endothelial layer barrier function in human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1). First, HMEC-1 were subjected to stimuli for 4 and 8 h. We tested their responses to DETA-NONOate, H2O2, high glucose, and angiotensin II, none of which relevantly affected the transcription of the connexin genes. Next, we tested inflammatory factors IL-6, interferon gamma (IFNγ), and TNFα. IFNγ (10 ng/mL) consistently induced Cx40 expression at 4 and 8 h to 10-20-fold when corrected for the control. TNFα and IL-6 resulted in small but significant depressions of Cx37 expression at 4 h. Two JAK inhibitors, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) (100-250 μM) and AG490 (100-250 μM), dose-dependently inhibited the induction of Cx40 expression by IFNγ. Subsequently, HMEC-1 were subjected to 10 ng/mL IFNγ for 60 h, and intercellular and transcellular impedance was monitored by electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS). In response to IFNγ, junctional-barrier impedance increased more than cellular-barrier impedance; this was prevented by AG490 (5 μM). In conclusion, IFNγ can strongly induce Cx40 expression and modify the barrier properties of the endothelial cell membrane through the JAK/STAT pathway. Moreover, the Cx37, Cx40, and Cx43 expression in endothelial cells is stable and, apart from IFNγ, not affected by a number of factors implicated in endothelial dysfunction and vascular diseases.
Keywords: JAK/STAT; cardiovascular risk factors; connexin; endothelial cell; interferon gamma.
Copyright © 2024 Zhuang, Mitrou, Kulak, Cupples and Braam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Heterogeneous expression of endothelial connexin (Cx) 37, Cx40, and Cx43 in rat large veins.Anat Sci Int. 2009 Sep;84(3):237-45. doi: 10.1007/s12565-009-0029-y. Epub 2009 Mar 26. Anat Sci Int. 2009. PMID: 19322632
-
Flow regulates intercellular communication in HAEC by assembling functional Cx40 and Cx37 gap junctional channels.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006 May;290(5):H2015-23. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00204.2005. Epub 2005 Dec 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16361362
-
Expression pattern of connexin gene products at the early developmental stages of the mouse cardiovascular system.Circ Res. 1997 Sep;81(3):423-37. doi: 10.1161/01.res.81.3.423. Circ Res. 1997. PMID: 9285645
-
Gap junctions and the connexin protein family.Cardiovasc Res. 2004 May 1;62(2):228-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.11.013. Cardiovasc Res. 2004. PMID: 15094343 Review.
-
Vascular gap junctions and implications for hypertension.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2004 Oct;31(10):659-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2004.04071.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15554905 Review.
References
-
- Bluyssen H. A., Rastmanesh M. M., Tilburgs C., Jie K., Wesseling S., Goumans M. J., et al. (2010a). IFN gamma-dependent SOCS3 expression inhibits IL-6-induced STAT3 phosphorylation and differentially affects IL-6 mediated transcriptional responses in endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 299, C354–C362. 10.1152/ajpcell.00513.2009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bluyssen H. A., Rastmanesh M. M., Tilburgs C., Jie K., Wesseling S., Goumans M. J., et al. (2010b). IFN gamma-dependent SOCS3 expression inhibits IL-6-induced STAT3 phosphorylation and differentially affects IL-6 mediated transcriptional responses in endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 299, C354–C362. 10.1152/ajpcell.00513.2009 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

