Extracellular vesicles as carriers for noncoding RNA-based regulation of macrophage/microglia polarization: an emerging candidate regulator for lung and traumatic brain injuries
- PMID: 38558799
- PMCID: PMC10978530
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343364
Extracellular vesicles as carriers for noncoding RNA-based regulation of macrophage/microglia polarization: an emerging candidate regulator for lung and traumatic brain injuries
Abstract
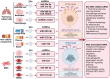
Macrophage/microglia function as immune defense and homeostatic cells that originate from bone marrow progenitor cells. Macrophage/microglia activation is historically divided into proinflammatory M1 or anti-inflammatory M2 states based on intracellular dynamics and protein production. The polarization of macrophages/microglia involves a pivotal impact in modulating the development of inflammatory disorders, namely lung and traumatic brain injuries. Recent evidence indicates shared signaling pathways in lung and traumatic brain injuries, regulated through non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) loaded into extracellular vesicles (EVs). This packaging protects ncRNAs from degradation. These vesicles are subcellular components released through a paracellular mechanism, constituting a group of nanoparticles that involve exosomes, microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies. EVs are characterized by a double-layered membrane and are abound with proteins, nucleic acids, and other bioactive compounds. ncRNAs are RNA molecules with functional roles, despite their absence of coding capacity. They actively participate in the regulation of mRNA expression and function through various mechanisms. Recent studies pointed out that selective packaging of ncRNAs into EVs plays a role in modulating distinct facets of macrophage/microglia polarization, under conditions of lung and traumatic brain injuries. This study will explore the latest findings regarding the role of EVs in the progression of lung and traumatic brain injuries, with a specific focus on the involvement of ncRNAs within these vesicles. The conclusion of this review will emphasize the clinical opportunities presented by EV-ncRNAs, underscoring their potential functions as both biomarkers and targets for therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; lung brain injury; macrophage/microglia polarization; noncoding RNA; traumatic brain injury.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Zhang, Pan, Hao and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sun B, Bai L, Li Q, Sun Y, Li M, Wang J, et al. Knockdown of angiopoietin-like 4 suppresses sepsis-induced acute lung injury by blocking the NF-κB pathway activation and hindering macrophage M1 polarization and pyroptosis. Toxicol Vitro an Int J published Assoc BIBRA. (2023) 94:105709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

