Formulating biopharmaceuticals using three-dimensional printing
- PMID: 38558867
- PMCID: PMC10979422
- DOI: 10.3389/jpps.2024.12797
Formulating biopharmaceuticals using three-dimensional printing
Abstract
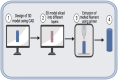
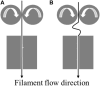
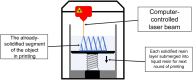
Additive manufacturing, commonly referred to as three-dimensional (3D) printing, has the potential to initiate a paradigm shift in the field of medicine and drug delivery. Ever since the advent of the first-ever United States Food and Drug Administration (US FDA)-approved 3D printed tablet, there has been an increased interest in the application of this technology in drug delivery and biomedical applications. 3D printing brings us one step closer to personalized medicine, hence rendering the "one size fits all" concept in drug dosing obsolete. In this review article, we focus on the recent developments in the field of modified drug delivery systems in which various types of additive manufacturing technologies are applied.
Keywords: additive manufacturing; drug delivery systems; fused deposition modelling; powder bed fusion; vat photopolymerization.
Copyright © 2024 Chan, Ranjitham Gopalakrishnan, Traore and Ho.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rett JP, Traore YL, Ho EA. Sustainable materials for fused deposition modeling 3D printing applications. Adv Eng Mater (2021) 23(7):2001472. 10.1002/adem.202001472 - DOI
-
- Herzberger J, Sirrine JM, Williams CB, Long TE. Polymer design for 3D printing elastomers: recent advances in structure, properties, and printing. Prog Polym Sci (2019) 97:101144. 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2019.101144 - DOI
-
- N Turner B, Strong R, A Gold S. A review of melt extrusion additive manufacturing processes: I. Process design and modeling. Rapid Prototyping J (2014) 20(3):192–204. 10.1108/RPJ-01-2013-0012 - DOI

