This is a preprint.
Synthetic dosage-compensating miRNA circuits allow precision gene therapy for Rett syndrome
- PMID: 38559034
- PMCID: PMC10980028
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.03.13.584179
Synthetic dosage-compensating miRNA circuits allow precision gene therapy for Rett syndrome
Abstract
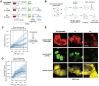
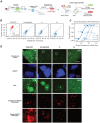
A longstanding challenge in gene therapy is expressing a dosage-sensitive gene within a tight therapeutic window. For example, loss of MECP2 function causes Rett syndrome, while its duplication causes MECP2 duplication syndrome. Viral gene delivery methods generate variable numbers of gene copies in individual cells, creating a need for gene dosage-invariant expression systems. Here, we introduce a compact miRNA-based, incoherent feed-forward loop circuit that achieves precise control of Mecp2 expression in cells and brains, and improves outcomes in an AAV-based mouse model of Rett syndrome gene therapy. Single molecule analysis of endogenous and ectopic Mecp2 mRNA revealed precise, sustained expression across a broad range of gene dosages. Delivered systemically in a brain-targeting AAV capsid, the circuit strongly suppressed Rett behavioral symptoms for over 24 weeks, outperforming an unregulated gene therapy. These results demonstrate that synthetic miRNA-based regulatory circuits can enable precise in vivo expression to improve the safety and efficacy of gene therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests A patent has been filed by the California Institute of Technology related to this work (US application number 17/100,857). M.B.E. is a scientific advisory board member or consultant at TeraCyte, Primordium, and Spatial Genomics.
Figures


References
-
- Mendell J. R., Al-Zaidy S., Shell R., Arnold W. D., Rodino-Klapac L. R., Prior T. W., Lowes L., Alfano L., Berry K., Church K., Kissel J. T., Nagendran S., L’Italien J., Sproule D. M., Wells C., Cardenas J. A., Heitzer M. D., Kaspar A., Corcoran S., Braun L., Likhite S., Miranda C., Meyer K., Foust K. D., Burghes A. H. M., Kaspar B. K., Single-Dose Gene-Replacement Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 377, 1713–1722 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Nathwani A. C., Reiss U. M., Tuddenham E. G. D., Rosales C., Chowdary P., McIntosh J., Della Peruta M., Lheriteau E., Patel N., Raj D., Riddell A., Pie J., Rangarajan S., Bevan D., Recht M., Shen Y.-M., Halka K. G., Basner-Tschakarjan E., Mingozzi F., High K. A., Allay J., Kay M. A., Ng C. Y. C., Zhou J., Cancio M., Morton C. L., Gray J. T., Srivastava D., Nienhuis A. W., Davidoff A. M., Long-term safety and efficacy of factor IX gene therapy in hemophilia B. N. Engl. J. Med. 371, 1994–2004 (2014). - PMC - PubMed
-
- George L. A., Sullivan S. K., Giermasz A., Rasko J. E. J., Samelson-Jones B. J., Ducore J., Cuker A., Sullivan L. M., Majumdar S., Teitel J., McGuinn C. E., Ragni M. V., Luk A. Y., Hui D., Wright J. F., Chen Y., Liu Y., Wachtel K., Winters A., Tiefenbacher S., Arruda V. R., van der Loo J. C. M., Zelenaia O., Takefman D., Carr M. E., Couto L. B., Anguela X. M., High K. A., Hemophilia B Gene Therapy with a High-Specific-Activity Factor IX Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 377, 2215–2227 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ozelo M. C., Mahlangu J., Pasi K. J., Giermasz A., Leavitt A. D., Laffan M., Symington E., Quon D. V., Wang J.-D., Peerlinck K., Pipe S. W., Madan B., Key N. S., Pierce G. F., O’Mahony B., Kaczmarek R., Henshaw J., Lawal A., Jayaram K., Huang M., Yang X., Wong W. Y., Kim B., GENEr8–1 Trial Group, Valoctocogene Roxaparvovec Gene Therapy for Hemophilia A. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 1013–1025 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Russell S., Bennett J., Wellman J. A., Chung D. C., Yu Z.-F., Tillman A., Wittes J., Pappas J., Elci O., McCague S., Cross D., Marshall K. A., Walshire J., Kehoe T. L., Reichert H., Davis M., Raffini L., George L. A., Hudson F. P., Dingfield L., Zhu X., Haller J. A., Sohn E. H., Mahajan V. B., Pfeifer W., Weckmann M., Johnson C., Gewaily D., Drack A., Stone E., Wachtel K., Simonelli F., Leroy B. P., Wright J. F., High K. A., Maguire A. M., Efficacy and safety of voretigene neparvovec (AAV2-hRPE65v2) in patients with RPE65-mediated inherited retinal dystrophy: a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 390, 849–860 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
