This is a preprint.
An expanded genetic toolkit for inducible expression and targeted gene silencing in Rickettsia parkeri
- PMID: 38559073
- PMCID: PMC10980030
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.03.15.585227
An expanded genetic toolkit for inducible expression and targeted gene silencing in Rickettsia parkeri
Update in
-
An expanded genetic toolkit for inducible expression and targeted gene silencing in Rickettsia parkeri.J Bacteriol. 2024 Jul 25;206(7):e0009124. doi: 10.1128/jb.00091-24. Epub 2024 Jun 6. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38842342 Free PMC article.
Abstract
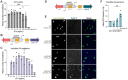
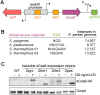
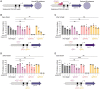
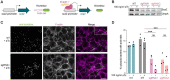
Pathogenic species within the Rickettsia genus are transmitted to humans through arthropod vectors and cause a spectrum of diseases ranging from mild to life-threatening. Despite rickettsiae posing an emerging global health risk, the genetic requirements of their infectious life cycles remain poorly understood. A major hurdle toward building this understanding has been the lack of efficient tools for genetic manipulation, owing to the technical difficulties associated with their obligate intracellular nature. To this end, we implemented the Tet-On system to enable conditional gene expression in Rickettsia parkeri. Using Tet-On, we show inducible expression of antibiotic resistance and a fluorescent reporter. We further used this inducible promoter to screen the ability of R. parkeri to express four variants of the catalytically dead Cas9 (dCas9). We demonstrate that all four dCas9 variants can be expressed in R. parkeri and used for CRISPR interference (CRISPRi)-mediated targeted gene knockdown. We show targeted knockdown of an antibiotic resistance gene as well as the endogenous virulence factor sca2. Altogether, we have developed systems for inducible gene expression and CRISPRi-mediated gene knockdown for the first time in rickettsiae, laying the groundwork for more scalable, targeted mechanistic investigations into their infectious life cycles.
Figures
References
-
- Intracellular Pathogens II: Rickettsiales. (ASM Press, Washington, DC, 2012). doi: 10.1128/9781555817336. - DOI
-
- Biggs H. M. et al. Diagnosis and Management of Tickborne Rickettsial Diseases: Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and Other Spotted Fever Group Rickettsioses, Ehrlichioses, and Anaplasmosis — United States: A Practical Guide for Health Care and Public Health Professionals. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 65, 1–44 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
