This is a preprint.
CSF proteomic profiling with amyloid/tau positivity identifies distinctive sex-different alteration of multiple proteins involved in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 38559166
- PMCID: PMC10980123
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.03.15.24304164
CSF proteomic profiling with amyloid/tau positivity identifies distinctive sex-different alteration of multiple proteins involved in Alzheimer's disease
Update in
-
CSF proteomic profiling with amyloid and tau pathology identifies distinctive sex-specific alteration of multiple proteins involved in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2026 Jan;22(1):e71063. doi: 10.1002/alz.71063. Alzheimers Dement. 2026. PMID: 41505229 Free PMC article.
Abstract
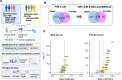
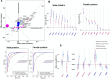
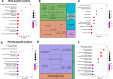
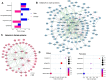
In Alzheimer's disease (AD), the most common cause of dementia, females have higher prevalence and faster progression, but sex-specific molecular findings in AD are limited. Here, we comprehensively examined and validated 7,006 aptamers targeting 6,162 proteins in cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) from 2,077 amyloid/tau positive cases and controls to identify sex-specific proteomic signatures of AD. In discovery (N=1,766), we identified 330 male-specific and 121 female-specific proteomic alternations in CSF (FDR <0.05). These sex-specific proteins strongly predicted amyloid/tau positivity (AUC=0.98 in males; 0.99 in females), significantly higher than those with age, sex, and APOE-ε4 (AUC=0.85). The identified sex-specific proteins were well validated (r≥0.5) in the Stanford study (N=108) and Emory study (N=148). Biological follow-up of these proteins led to sex differences in cell-type specificity, pathways, interaction networks, and drug targets. Male-specific proteins, enriched in astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, were involved in postsynaptic and axon-genesis. The male network exhibited direct connections among 152 proteins and highlighted PTEN, NOTCH1, FYN, and MAPK8 as hubs. Drug target suggested melatonin (used for sleep-wake cycle regulation), nabumetone (used for pain), daunorubicin, and verteporfin for treating AD males. In contrast, female-specific proteins, enriched in neurons, were involved in phosphoserine residue binding including cytokine activities. The female network exhibits strong connections among 51 proteins and highlighted JUN and 14-3-3 proteins (YWHAG and YWHAZ) as hubs. Drug target suggested biperiden (for muscle control of Parkinson's disease), nimodipine (for cerebral vasospasm), quinostatin and ethaverine for treating AD females. Together, our findings provide mechanistic understanding of sex differences for AD risk and insights into clinically translatable interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest CC has received research support from: GSK and EISAI. AR and MB have received research support from Grifols, Roche, Araclon and Janssen. The funders of the study had no role in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; or in the decision to submit the paper for publication. CC is a member of the advisory board of Circular Genomics and owns stocks.
Figures
References
-
- van Dyck C.H., et al. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N Engl J Med 388, 9–21 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
