This is a preprint.
An integrative systems-biology approach defines mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease neurodegeneration
- PMID: 38559190
- PMCID: PMC10980014
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.03.17.585262
An integrative systems-biology approach defines mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease neurodegeneration
Update in
-
An integrative systems-biology approach defines mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease neurodegeneration.Nat Commun. 2025 May 20;16(1):4441. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59654-w. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40393985 Free PMC article.
Abstract
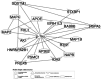
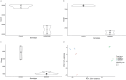
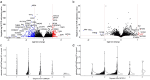
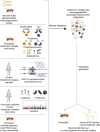
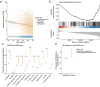
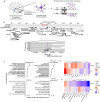
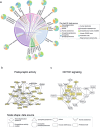
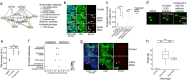
Despite years of intense investigation, the mechanisms underlying neuronal death in Alzheimer's disease, the most common neurodegenerative disorder, remain incompletely understood. To define relevant pathways, we integrated the results of an unbiased, genome-scale forward genetic screen for age-associated neurodegeneration in Drosophila with human and Drosophila Alzheimer's disease-associated multi-omics. We measured proteomics, phosphoproteomics, and metabolomics in Drosophila models of Alzheimer's disease and identified Alzheimer's disease human genetic variants that modify expression in disease-vulnerable neurons. We used a network optimization approach to integrate these data with previously published Alzheimer's disease multi-omic data. We computationally predicted and experimentally demonstrated how HNRNPA2B1 and MEPCE enhance tau-mediated neurotoxicity. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the screen hits CSNK2A1 and NOTCH1 regulate DNA damage in Drosophila and human iPSC-derived neural progenitor cells. Our work identifies candidate pathways that could be targeted to ameliorate neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Goedert M. & Spillantini M. G. A Century of Alzheimer’s Disease. Science 314, 777–780 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Lee V. M.-Y., Goedert M. & Trojanowski J. Q. Neurodegenerative Tauopathies. Annu. Rev. Neurosci 24, 1121–1159 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Hutton M. et al. Association of missense and 5Q-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 393, 702–705 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- U01 MH116442/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109897/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH057881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109677/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R24 OD030002/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032990/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH066392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG061356/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH075916/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072980/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P40 OD018537/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057331/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS080820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH084053/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- ZIC MH002903/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG002219/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201300031C/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH128366/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH093725/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS072026/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025711/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH110921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017216/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080405/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036836/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
