Bee chitosan nanoparticles loaded with apitoxin as a novel approach to eradication of common human bacterial, fungal pathogens and treating cancer
- PMID: 38559346
- PMCID: PMC10978808
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1345478
Bee chitosan nanoparticles loaded with apitoxin as a novel approach to eradication of common human bacterial, fungal pathogens and treating cancer
Abstract
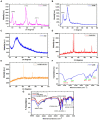
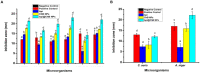
Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest medical challenges because of the rising frequency of opportunistic human microbial infections across the globe. This study aimed to extract chitosan from the exoskeletons of dead bees and load it with bee venom (commercially available as Apitoxin [Api]). Then, the ionotropic gelation method would be used to form nanoparticles that could be a novel drug-delivery system that might eradicate eight common human pathogens (i.e., two fungal and six bacteria strains). It might also be used to treat the human colon cancer cell line (Caco2 ATCC ATP-37) and human liver cancer cell line (HepG2ATCC HB-8065) cancer cell lines. The x-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), and dynamic light scattering (DLS) properties, ζ-potentials, and surface appearances of the nanoparticles were evaluated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). FTIR and XRD validated that the Api was successfully encapsulated in the chitosan nanoparticles (ChB NPs). According to the TEM, the ChB NPs and the ChB NPs loaded with Apitoxin (Api@ChB NPs) had a spherical shape and uniform size distribution, with non-aggregation, for an average size of approximately 182 and 274 ± 3.8 nm, respectively, and their Zeta potential values were 37.8 ± 1.2 mV and - 10.9 mV, respectively. The Api@ChB NPs had the greatest inhibitory effect against all tested strains compared with the ChB NPs and Api alone. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of the Api, ChB NPs, and Api@ChB NPs were evaluated against the offer mentioned colony forming units (CFU/mL), and their lowest MIC values were 30, 25, and 12.5 μg mL-1, respectively, against Enterococcus faecalis. Identifiable morphological features of apoptosis were observed by 3 T3 Phototox software after Api@ChB NPs had been used to treat the normal Vero ATCC CCL-81, Caco2 ATCC ATP-37, and HepG2 ATCC HB-8065 cancer cell lines for 24 h. The morphological changes were clear in a concentration-dependent manner, and the ability of the cells was 250 to 500 μg mL-1. These results revealed that Api@ChB NPs may be a promising natural nanotreatment for common human pathogens.
Keywords: Apis mellifera; antimicrobial resistance; apitoxin; bee’s chitosan NPs; colon cancer; drug delivery system.
Copyright © 2024 Sharaf, Zahra, Alharbi, Mekky, Shehata, Alkhudhayri, Ali, Al Suhaimi, Zakai, Al Harthi and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer GMEE declared a shared affiliation with the authors MS, AZ, AM, and AS to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antifungal and antibiofilm activities of bee venom loaded on chitosan nanoparticles: a novel approach for combating fungal human pathogens.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Oct 25;38(12):244. doi: 10.1007/s11274-022-03425-y. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36280608 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenic nanosilver bearing antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities and its potential for application in agriculture and industry.Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 20;14:1125685. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1125685. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36891391 Free PMC article.
-
Moringa concanensis-Mediated Synthesis and Characterizations of Ciprofloxacin Encapsulated into Ag/TiO2/Fe2O3/CS Nanocomposite: A Therapeutic Solution against Multidrug Resistant E. coli Strains of Livestock Infectious Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 17;14(8):1719. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081719. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015345 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activity of apitoxin, melittin and phospholipase A₂ of honey bee (Apis mellifera) venom against oral pathogens.An Acad Bras Cienc. 2015 Mar;87(1):147-55. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765201520130511. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2015. PMID: 25806982
-
Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxic and epigenetic effects of tannic acid-loaded chitosan nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 6;14(1):30405. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80771-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39638815 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Propolis extract nanoparticles alleviate diabetes-induced reproductive dysfunction in male rats: antidiabetic, antioxidant, and steroidogenesis modulatory role.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 23;14(1):30607. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81949-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39715797 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of honey bee venom-loaded calcium oxide nanocomposites and evaluation of their cytotoxic (MCF-7) and antifungal activity.Discov Nano. 2025 Jul 31;20(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s11671-025-04322-7. Discov Nano. 2025. PMID: 40745502 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the power of bee venom for therapeutic and regenerative medical applications: an updated review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 18;15:1412245. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1412245. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39092234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in bio-polymer coatings for probiotic microencapsulation: chitosan and beyond for enhanced stability and controlled release.Des Monomers Polym. 2024 Dec 31;28(1):1-34. doi: 10.1080/15685551.2024.2448122. eCollection 2025. Des Monomers Polym. 2024. PMID: 39777298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antifungal Nanocomposites from Honeybee Chitosan and Royal Jelly-Mediated Nanosilver for Suppressing Biofilm and Hyphal Formation of Candida albicans.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;17(14):1916. doi: 10.3390/polym17141916. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alalawy A. I., El Rabey H. A., Almutairi F. M., Tayel A. A., Al-Duais M. A., Zidan N. S., et al. . (2020). Effectual anticancer potentiality of loaded bee venom onto fungal chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Polymer Sci. 2020, 1–9. doi: 10.1155/2020/2785304 - DOI
-
- Amor I. B., Hemmami H., Laouini S. E., Abdelaziz A. G. (2023). Barhoum and biorefinery, 1–11.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

