Improved Side Effect Profile of Alternate-Day Dosing of Lenalidomide
- PMID: 38559519
- PMCID: PMC10981840
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.55317
Improved Side Effect Profile of Alternate-Day Dosing of Lenalidomide
Abstract
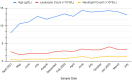
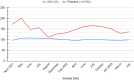
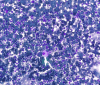
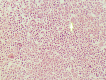
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is a heterogeneous hematological condition associated with cytopenia, inadequate blood cell synthesis, and the risk of developing acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Patients are divided into risk groups according to the International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) to help direct therapy. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation, despite its limitations, is curative. Medical management, such as the use of lenalidomide, has potential benefits but can cause adverse effects that require dose regimen modification. Lenalidomide is approved for low-risk MDS with 5q deletion (5q- MDS). In this case study, a 79-year-old woman with 5q- MDS was switched from a daily regimen to an alternate-day lenalidomide dose schedule to achieve complete remission with fewer adverse effects. The management of hematological toxicity and the mechanisms of action of lenalidomide are discussed. We recommend individualized treatment strategies and additional research to improve MDS management.
Keywords: alternate day dosing; del(5q); lenalidomide; myelodysplastic syndrome (mds); resource limited setting.
Copyright © 2024, Lawal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Myelodysplastic syndromes. Li H, Hu F, Gale RP, Sekeres MA, Liang Y. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022;8:74. - PubMed
-
- New approaches to myelodysplastic syndrome treatment. Bazinet A, Bravo GM. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022;23:668–687. - PubMed
-
- How we manage adults with myelodysplastic syndrome. Fenaux P, Platzbecker U, Ades L. Br J Haematol. 2020;189:1016–1027. - PubMed
-
- Treatment of MDS. Platzbecker U. Blood. 2019;133:1096–1107. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
