A Case in Which HLA-DR4 is Involved in the Development of Complex Immune-Related Endocrinological Adverse Events following Combination Therapy with Nivolumab and Ipilimumab
- PMID: 38559614
- PMCID: PMC10980546
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/4662803
A Case in Which HLA-DR4 is Involved in the Development of Complex Immune-Related Endocrinological Adverse Events following Combination Therapy with Nivolumab and Ipilimumab
Abstract
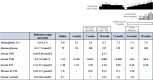
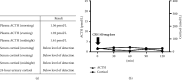
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have become a focal point in cancer immunotherapy, though their utilization is also linked to the occurrence of diverse immune-related adverse events (irAEs). Herein, we present details of a 42-year-old woman diagnosed with a malignant vaginal melanoma who underwent ICI therapy with the combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab. Approximately two months after initiating therapy, the patient manifested destructive thyroiditis and fulminant type 1 diabetes mellitus, thus necessitating intensive insulin therapy. Following the onset of adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency, frequent hypoglycemic episodes prompted the initiation of replacement therapy with hydrocortisone. Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DNA typing revealed the presence of HLA-DRB1∗04 : 05 and DQB1∗04 : 01. HLA-DR4 has been suggested to be associated with the development of multiple endocrine irAEs. This is the first reported case of three endocrine irAEs occurring within a short period, in which the presence of HLA-DR4 may have contributed to the pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2024 Yonekazu Kidawara et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency and thyroiditis associated with nivolumab therapy in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2019 Mar 26;13(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13256-019-2002-2. J Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30909965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fulminant Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Developed about Half a Year after Discontinuation of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Combination Therapy with Nivolumab and Ipilimumab: A Case Report.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2021 Aug;254(4):253-256. doi: 10.1620/tjem.254.253. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 34373422
-
Case Report: A Variety of Immune-Related Adverse Events Triggered by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in a Subject With Malignant Melanoma: Destructive Thyroiditis, Aseptic Meningitis and Isolated ACTH Deficiency.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 12;12:722586. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.722586. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34712202 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Human Leukocyte Antigen DR Alleles, Immune-Related Adverse Events, and Survival Associated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Use Among Patients With Advanced Malignant Melanoma.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Dec 1;5(12):e2246400. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.46400. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 36512357 Free PMC article.
-
New insight in endocrine-related adverse events associated to immune checkpoint blockade.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jan;34(1):101370. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2019.101370. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 31983543 Review.
Cited by
-
Sintilimab-induced diabetes mellitus and thyroid dysfunction in patient with gastric adenocarcinoma: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 16;104(20):e42490. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042490. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40388765 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

