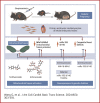
Small Molecule Activators of Mitochondrial Fusion Prevent Congenital Heart Defects Induced by Maternal Diabetes
- PMID: 38559623
- PMCID: PMC10978414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.11.008
Small Molecule Activators of Mitochondrial Fusion Prevent Congenital Heart Defects Induced by Maternal Diabetes
Abstract
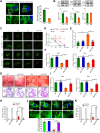
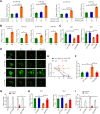
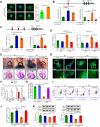
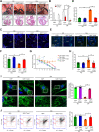
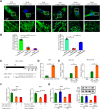
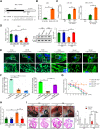
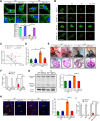
Most congenital heart defect (CHD) cases are attributed to nongenetic factors; however, the mechanisms underlying nongenetic factor-induced CHDs are elusive. Maternal diabetes is one of the nongenetic factors, and this study aimed to determine whether impaired mitochondrial fusion contributes to maternal diabetes-induced CHDs and if mitochondrial fusion activators, teriflunomide and echinacoside, could reduce CHD incidence in diabetic pregnancy. We demonstrated maternal diabetes-activated FoxO3a increases miR-140 and miR-195, which in turn represses Mfn1 and Mfn2, leading to mitochondrial fusion defects and CHDs. Two mitochondrial fusion activators are effective in preventing CHDs in diabetic pregnancy.
Keywords: congenital heart defect; maternal diabetes; microRNA; mitochondrial fusion; mitofusin 1; mitofusin 2.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was financially supported by National Institutes of Health grants R01DK083243, R01DK101972, R01DK103024, R01HL131737, R01HL134368, R01HL139060, R01HL153141, and R01HL151108. The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Mathews T.J., Driscoll A.K. Trends in infant mortality in the United States, 2005-2014. NCHS Data Brief. 2017;(279):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Virani S.S., Alonso A., Benjamin E.J., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139–e596. - PubMed
-
- Botto L.D., Mulinare J., Erickson J.D. Occurrence of congenital heart defects in relation to maternal mulitivitamin use. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;151:878–884. - PubMed
-
- Jenkins K.J., Correa A., Feinstein J.A., et al. Noninherited risk factors and congenital cardiovascular defects: current knowledge: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young: endorsed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Circulation. 2007;115:2995–3014. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

