Little Ironweed and Java Tea in Herbal Toothpaste Reduced Dentine Permeability: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 38559639
- PMCID: PMC10980310
- DOI: 10.4103/jispcd.jispcd_67_23
Little Ironweed and Java Tea in Herbal Toothpaste Reduced Dentine Permeability: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
Aim: To determine the effect of an herbal toothpaste containing Little Ironweed and Java Tea, on reducing dentine permeability in vitro.
Materials and methods: Dentine discs from human mandibular third molars were divided into three groups and brushed with herbal toothpaste, nonherbal toothpaste, or deionized water. Each group was immersed in artificial saliva (AS) or 6% citric acid. The permeability of each dentine disc was evaluated before and after saliva or acid challenge using a fluid filtration system. The morphology of dentine discs after treatment was observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The mean permeabilities were statistically analyzed using analysis of variance and Tukey's test.
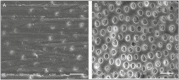
Results: The nonherbal and herbal toothpaste groups demonstrated reduced dentine permeability. AS immersion decreased dentine permeability in both toothpaste groups with values lower than the control group. Dentine permeability values increased after acid immersion in the toothpaste groups and were similar to each other. SEM revealed small granular crystal-like and round particles on the dentine surface and opening of dentinal tubules of both toothpaste groups. More dentinal tubules were opened after brushing with deionized water.
Conclusions: The reduction of dentine permeability caused by the herbal toothpaste was similar to that of the nonherbal toothpaste after brushing and the simulated oral conditions. Both herbal plants have the possibility to alleviate clinical hypersensitivity by reducing dentine permeability. Little Ironweed and Java Tea in the toothpaste composition is a potential choice for treating hypersensitive dentine.
Keywords: Dentine permeability; herbal and nonherbal toothpastes; tubules occlusion.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Changes in the permeability and morphology of dentine surfaces after brushing with a Thai herbal toothpaste: A preliminary study.Eur J Dent. 2016 Apr-Jun;10(2):239-244. doi: 10.4103/1305-7456.178319. Eur J Dent. 2016. PMID: 27095904 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of desensitising toothpastes on dentinal tubule occlusion: a dentine permeability measurement and SEM in vitro study.J Dent. 2010 May;38(5):400-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2010.01.007. Epub 2010 Jan 25. J Dent. 2010. PMID: 20097250
-
Effect of a novel bioactive glass-ceramic on dentinal tubule occlusion: an in vitro study.Aust Dent J. 2015 Mar;60(1):96-103. doi: 10.1111/adj.12241. Aust Dent J. 2015. PMID: 25329231
-
The role of toothpaste in the aetiology and treatment of dentine hypersensitivity.Monogr Oral Sci. 2013;23:75-87. doi: 10.1159/000350477. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Monogr Oral Sci. 2013. PMID: 23817061 Review.
-
Can tooth brushing damage your health? Effects on oral and dental tissues.Int Dent J. 2003;53 Suppl 3:177-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1875-595x.2003.tb00768.x. Int Dent J. 2003. PMID: 12875306 Review.
References
-
- Chen CY, Hasselgren G. Lack of fluid movement between dentin tubule and pulp tissue: An in vitro study. Dent Hypotheses. 2022;13:67–9.
-
- Rajguru SA, Padhye AM, Gupta HS. Effects of two desensitizing dentifrices on dentinal tubule occlusion with citric acid challenge: Confocal laser scanning microscopy study. Indian J Dent Res. 2017;28:450–6. - PubMed
-
- Freda NM, Veitz-Keenan A. Calcium sodium phosphosilicate had some benefit on dentine hypersensitivity. Evid Based Dent. 2016;17:12–3. - PubMed
-
- Misra TN, Singh RS, Upadhyay J, Srivastava R. Chemical constituents of Vernonia cinerea, Part I. Isolation and spectral studies of triterpenes. J Nat Prod. 1984;47:368–72.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

