Ultrasound principles and instrumentation
- PMID: 38559744
- PMCID: PMC10979256
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sopen.2024.02.005
Ultrasound principles and instrumentation
Abstract
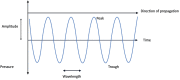
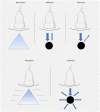
Ultrasound (US) is a fundamental and inexpensive tool both for the prompt diagnosis and for the study of diverse medical conditions. Its widespread use is partly due to the availability of US devices in the daily practice of physicians. US can be performed in real-time and is instrumental in the generation of clinical algorithms for the management of situations like trauma. It also constitutes a primary approach for the study of oncological diseases, and a guidance tool for interventions such as percutaneous drainages. In addition, and specifically for HPB surgeons, US is an essential tool in the operating room: intraoperative (either open or laparoscopic) US is necessary for the accurate determination of the stage, location, number, and margins of tumors within the liver, pancreas, or biliary tree. On another note, reading and understanding US images are skills that require time and training, which should be taught during surgical residencies. However, this is not customary in most residencies globally. This chapter offers a concise yet comprehensive elucidation of the basic principles of ultrasonography, the instruments required to perform an ultrasonic assessment of a patient, and the basic ultrasound controls.
Keywords: Biliary; Liver; Pancreas; Physics; US; Ultrasound.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




References
-
- Powles A.E., Martin D.J., Wells I.T., Goodwin C.R. Physics of ultrasound. Anaesth Intensive Care Med. 2018 Apr 1;19(4):202–205. http://www.anaesthesiajournal.co.uk/article/S1472029918300171/fulltext [cited 2023 May 31]. Available from:
-
- Nicolaides A., Beach K.W., Kyriacou E., Pattichis C.S. Ultrasound and carotid bifurcation atherosclerosis. Vol. 9781848826. Springer London LTD; 2013. Ultrasound and carotid bifurcation atherosclerosis; pp. 1–649.
-
- Carovac A., Smajlovic F., Junuzovic D. Application of ultrasound in medicine. Acta Inform Medica. 2011;19(3):168. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23408755 [cited 2023 Jun 1]. Available from: - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hagopian Ellen J., Machi J., editors. Abdominal ultrasound for surgeons. Springer; 2014. Chapter 1.
-
- Paltiel H.J., Lee E.Y. Vol. 1034. 2021. Pediatric ultrasound.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

