SNSVM: SqueezeNet-Guided SVM for Breast Cancer Diagnosis
- PMID: 38559807
- PMCID: PMC7615775
- DOI: 10.32604/cmc.2023.041191
SNSVM: SqueezeNet-Guided SVM for Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Abstract
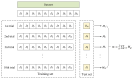
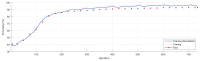
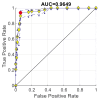
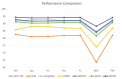
Breast cancer is a major public health concern that affects women worldwide. It is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women, and early detection is crucial for successful treatment. Unfortunately, breast cancer can often go undetected until it has reached advanced stages, making it more difficult to treat. Therefore, there is a pressing need for accurate and efficient diagnostic tools to detect breast cancer at an early stage. The proposed approach utilizes SqueezeNet with fire modules and complex bypass to extract informative features from mammography images. The extracted features are then utilized to train a support vector machine (SVM) for mammography image classification. The SqueezeNet-guided SVM model, known as SNSVM, achieved promising results, with an accuracy of 94.10% and a sensitivity of 94.30%. A 10-fold cross-validation was performed to ensure the robustness of the results, and the mean and standard deviation of various performance indicators were calculated across multiple runs. This model also outperforms state-of-the-art models in all performance indicators, indicating its superior performance. This demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed approach for breast cancer diagnosis using mammography images. The superior performance of the proposed model across all indicators makes it a promising tool for early breast cancer diagnosis. This may have significant implications for reducing breast cancer mortality rates.
Keywords: SqueezeNet; breast cancer diagnosis; support vector machine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
Figures
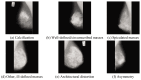
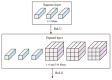
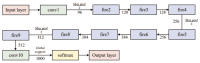
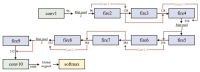

References
-
- Aldrich J, Ekpo P, Rupji M, Switchenko JM, Torres MA, et al. Racial disparities in clinical outcomes on investigator-initiated breast cancer clinical trials at an urban medical center. Clinical Breast Cancer. 2023;23(1):38–44. - PubMed
-
- Dan WC, Guo XY, Zhang GZ, Wang SL, Deng M, et al. Integrative analyses of radiation-related genes and biomarkers associated with breast cancer. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2023;27(1):256–274. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
