EIDD-1931 Treatment Tweaks CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 in Arthritic Rats to Expedite Drug Interaction: Implication in Oral Therapy of Molnupiravir
- PMID: 38559969
- PMCID: PMC10976394
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09287
EIDD-1931 Treatment Tweaks CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 in Arthritic Rats to Expedite Drug Interaction: Implication in Oral Therapy of Molnupiravir
Abstract
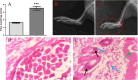
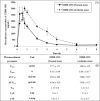
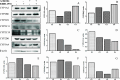
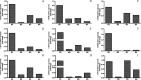
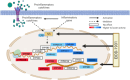
EIDD-1931 is the active form of molnupiravir, an orally effective drug approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) against COVID-19. Pharmacokinetic alteration can cause untoward drug interaction (drug-drug/disease-drug), but hardly any information is known about this recently approved drug. Therefore, we first investigated the impact of the arthritis state on the oral pharmacokinetics of EIDD-1931 using a widely accepted complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced rat model of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) after ascertaining the disease occurrence by paw swelling measurement and X-ray examination. Comparative oral pharmacokinetic assessment of EIDD-1931 (normal state vs arthritis state) showed that overall plasma exposure was augmented (1.7-fold) with reduced clearance (0.54-fold), suggesting its likelihood of dose adjustment in arthritis conditions. In order to elucidate the effect of EIDD-1931 treatment at a therapeutic regime (normal state vs arthritis state) on USFDA-recommended panel of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes (CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4) for drug interaction using the same disease model, we monitored protein and mRNA expressions (rat homologs) in liver tissue by western blotting (WB) and real time-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), respectively. Results reveal that EIDD-1931 treatment could strongly influence CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 among experimental proteins/mRNAs. Although CYP2C8 regulation upon EIDD-1931 treatment resembles similar behavior under the arthritis state, results dictate a potentially reverse phenomenon for CYP3A4. Moreover, the lack of any CYP inhibitory effect by EIDD-1931 in human/rat liver microsomes (HLM/RLM) helps to ascertain EIDD-1931 treatment-mediated disease-drug interaction and the possibility of drug-drug interaction with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) upon coadministration. As elevated proinflammatory cytokine levels are prevalent in RA and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB) and nuclear receptors control CYP expressions, further studies should focus on understanding the regulation of affected CYPs to subside unexpected drug interaction.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of Disease States on the Oral Pharmacokinetics of EIDD-1931 (an Active Form of Molnupiravir) in Rats for Implication in the Dose Adjustment.Mol Pharm. 2023 Sep 4;20(9):4597-4610. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00314. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Mol Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37527414
-
Evaluation of Herb-Drug Interaction of Synacinn™ and Individual Biomarker through Cytochrome 450 Inhibition Assay.Drug Metab Lett. 2018;12(1):62-67. doi: 10.2174/1872312812666180314112457. Drug Metab Lett. 2018. PMID: 29542427
-
In vitro and in vivo assessment of the effect of dalcetrapib on a panel of CYP substrates.Curr Med Res Opin. 2009 Apr;25(4):891-902. doi: 10.1185/03007990902790928. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. PMID: 19245299
-
Effect of genetic polymorphisms in cytochrome p450 (CYP) 2C9 and CYP2C8 on the pharmacokinetics of oral antidiabetic drugs: clinical relevance.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005;44(12):1209-25. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200544120-00002. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005. PMID: 16372821 Review.
-
Human Cytochrome P450 1, 2, 3 Families as Pharmacogenes with Emphases on Their Antimalarial and Antituberculosis Drugs and Prevalent African Alleles.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 8;24(4):3383. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043383. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Scientific group Rheumatic diseases World Health Organization, 1992.
-
- WHO Musculoskeletal Health. World Health Organization; 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
