Nitrogen Minimization in Hydrothermal Liquefaction Biocrude from Sewage Sludge with Green Extraction Solvents
- PMID: 38560002
- PMCID: PMC10975588
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00455
Nitrogen Minimization in Hydrothermal Liquefaction Biocrude from Sewage Sludge with Green Extraction Solvents
Abstract
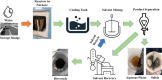
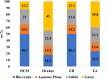
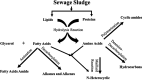
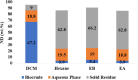
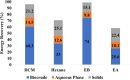
This study explored the effectiveness of hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) in converting sewage sludge (SS) into high-quality biocrude. It scrutinized the influence of various solvents, including conventional choices like dichloromethane (DCM) and hexane, alongside environmentally friendly alternatives, such as ethyl butyrate (EB) and ethyl acetate (EA). HTL experiments, conducted at 350 °C for 60 min in a 20 mL batch reactor, include solvent-based biocrude extraction. Notably, EB showed the highest extraction yield (50.1 wt %), the lowest nitrogen distribution (5.4% with 0.32 wt %), and a remarkable 74% energy recovery (ER), setting a noteworthy benchmark in nitrogen reduction. GCMS analysis reveals EB-derived biocrude's superiority in having the least heteroatoms and nitrogenous compounds compared to hexane, EA, and DCM. Solid residues from hexane, EB, and EA displayed the highest nitrogen distribution range (62-68%), hinting at potential applications in further processes. These findings significantly inform solvent selection for efficient and sustainable waste-to-energy conversion. While promising, the study emphasizes the need to explore solvent-solute interactions further to optimize biocrude quality, highlighting the pivotal role of solvent choice in advancing clean, cost-effective waste-to-energy technologies.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Oladejo J.; Shi K.; Luo X.; Yang G.; Wu T. A Review of Sludge-to-Energy Recovery Methods. Energies 2019, 12 (1), 60. 10.3390/en12010060. - DOI
-
- Djandja O. S.; Yin L.-X.; Wang Z.; Duan P.-G. From Wastewater Treatment to Resources Recovery through Hydrothermal Treatments of Municipal Sewage Sludge: A Critical Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 151, 101–127. 10.1016/j.psep.2021.05.006. - DOI
-
- Usman M.; Cheng S.; Cross J. S. Biodiesel Production from Wet Sewage Sludge and Reduced CO2 Emissions Compared to Incineration in Tokyo, Japan. Fuel 2023, 341, 127614. 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127614. - DOI
-
- Usman M.; Cheng S.; Boonyubol S.; Cross J. S. From biomass to biocrude: Innovations in hydrothermal liquefaction and upgrading. Energy Convers. Manage. 2024, 302, 118093. 10.1016/j.enconman.2024.118093. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
