Nalmefene, an opioid receptor modulator, aggravates atherosclerotic plaque formation in apolipoprotein E knockout mice by enhancing oxidized low-density lipoprotein uptake in macrophages
- PMID: 38560051
- PMCID: PMC10979050
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101688
Nalmefene, an opioid receptor modulator, aggravates atherosclerotic plaque formation in apolipoprotein E knockout mice by enhancing oxidized low-density lipoprotein uptake in macrophages
Abstract
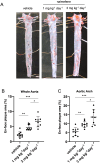
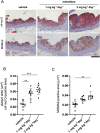
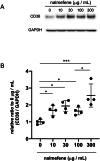
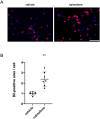
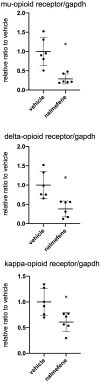
Nalmefene, an antagonist of mu- and delta-opioid receptors and a partial agonist of kappa-opioid receptors, has shown promise in reducing alcohol consumption among patients with alcohol dependence. Opioid receptors play pivotal roles in various physiological processes, including those related to peripheral inflammatory diseases such as colitis and arthritis, as well as functions in the immune system and phagocytosis. Atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disease, progresses through the phagocytosis and uptake of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) by macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques. Despite this knowledge, it remains unclear whether nalmefene influences the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events. This study aims to elucidate the impact of nalmefene on atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E knockout (ApoE KO) mice and peritoneal macrophages in vitro. In this experiment, 8-week-old male ApoE KO mice were fed a high-fat diet intraperitoneally administered either vehicle (saline) or nalmefene (1 mg and 3 mg kg-1 day-1) for 21 days. Oil red O-staining and immunohistochemistry with an anti-MOMA2 (monocyte/macrophage) antibody showed that a dose-dependent increase in atherosclerotic plaque formation and augmentation of macrophage-rich plaque formation in ApoE-KO mice. Further investigations focused on the effects of nalmefene on the expression of scavenger receptor CD36 in RAW264.7 cells, conducted through western blotting analysis. Nalmefene demonstrated a significant increase in CD36 protein expression in RAW264.7 cells. To explore the impact on oxidized LDL uptake in peritoneal macrophages, cells were treated with nalmefene (300 μg/mL) for 24 h, followed by the addition of DiI-labeled oxLDL (DiI-oxLDL) for 4 h. Nalmefene significantly enhanced DiI-oxLDL uptake in macrophages. Additionally, treatment with nalmefene (300 μg/mL) for 24 h decreased the mRNA expression of mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors in RAW264.7 cells. In conclusion, nalmefene may augment oxLDL uptake by macrophages through increased CD36 expression and decreased opioid receptor, thereby contributing to atherosclerotic plaque formation and vulnerability. Consequently, the use of nalmefene may be associated with an elevated risk of cardiovascular events.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Nalmefene; Opioid receptors; Side effect.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Varenicline enhances oxidized LDL uptake by increasing expression of LOX-1 and CD36 scavenger receptors through α7 nAChR in macrophages.Toxicology. 2017 Apr 1;380:62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2017.02.006. Epub 2017 Feb 12. Toxicology. 2017. PMID: 28202387
-
Varenicline aggravates atherosclerotic plaque formation in nicotine-pretreated ApoE knockout mice due to enhanced oxLDL uptake by macrophages through downregulation of ABCA1 and ABCG1 expression.J Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Jan;142(1):9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2019.11.002. Epub 2019 Nov 14. J Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31771811
-
BMP4 is increased in the aortas of diabetic ApoE knockout mice and enhances uptake of oxidized low density lipoprotein into peritoneal macrophages.J Inflamm (Lond). 2013 Oct 9;10(1):32. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-10-32. J Inflamm (Lond). 2013. PMID: 24107300 Free PMC article.
-
[Pharmacological profile and clinical findings of nalmefene (Selincro®) for reducing alcohol consumption in patients with alcohol dependence].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2020;155(2):113-119. doi: 10.1254/fpj.19136. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2020. PMID: 32115477 Review. Japanese.
-
CD36, a scavenger receptor implicated in atherosclerosis.Exp Mol Med. 2014 Jun 6;46(6):e99. doi: 10.1038/emm.2014.38. Exp Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24903227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Morphine acts in vitro to directly prime nociceptors.Mol Pain. 2024 Jan-Dec;20:17448069241260348. doi: 10.1177/17448069241260348. Mol Pain. 2024. PMID: 38828868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roerecke M., Rehm J. Alcohol consumption, drinking patterns, and ischemic heart disease: a narrative review of meta-analyses and a systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of heavy drinking occasions on risk for moderate drinkers. BMC Med. 2014;12:182. doi: 10.1186/s12916-014-0182-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rehm J., Baliunas D., Borges G.L.G., Graham K., Irving H., Kehoe T., Parry C.D., Patra J., Popova S., Poznyak V., Roerecke M., Room R., Samokhvalov A.V., Taylor B. The relation between different dimensions of alcohol consumption and burden of disease: an overview. Addiction. 2010;105:817–843. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2010.02899.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Calleja‐Conde J., Echeverry‐Alzate V., Giné E., Bühler K.M., Nadal R., Maldonado R., Rodríguez de Fonseca F., Gual A., López‐Moreno J.A. Nalmefene is effective at reducing alcohol seeking, treating alcohol‐cocaine interactions and reducing alcohol‐induced histone deacetylases gene expression in blood. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016;173:2490–2505. doi: 10.1111/bph.13526. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

