Intraspinal Extradural Degenerative Cervical Cyst Treated by Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion: A Surgical Alternative to the Posterior Approach, about One Case
- PMID: 38560330
- PMCID: PMC10976530
- DOI: 10.13107/jocr.2024.v14.i03.4290
Intraspinal Extradural Degenerative Cervical Cyst Treated by Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion: A Surgical Alternative to the Posterior Approach, about One Case
Abstract
Introduction: Intraspinal extradural arthrosynovial cysts, which belong to the spectrum of degenerative spinal diseases are mainly located at lumbar level and their location at cervical level joint is therefore unusual. The most common surgical approach for symptomatic arthrosynovial cervical cyst remains a direct resection of the cyst by a cervical hemilaminectomy with or without a posterior arthrodesis. However, another surgical approach may also be discussed when considering the cyst as a result of a local spinal instability or hypermobility.
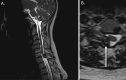
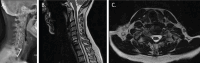
Case report: We report in this work the case of a patient with cervical radiculopathy due to intraspinal extradural compressive arthrosynovial cervical cyst which was treated by anterior discectomy and fusion without direct resection of the cyst. The post-operative radiological control performed at 3 months showed a complete regression of the cyst with a patient pain-free. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of intraspinal cervical degenerative cyst at C7-T1 level treated by anterior approach and fusion without direct cyst resection.
Conclusion: For the treatment of a joint spinal cervical cyst, the anterior approach is a relevant option that gives the advantages to respect the posterior cervical muscles and articular structures.
Keywords: Intraspinal cervical cyst; anterior discectomy and fusion; hemilaminectomy.
Copyright: © Indian Orthopaedic Research Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Nil
Figures
References
-
- Baker WM. On the formation of synovial cysts in the leg in connection with disease of the knee-joint. 1877. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;299:2–10. - PubMed
-
- Yarde WL, Arnold PM, Kepes JJ, O'Boynick PL, Wilkinson SB, Batnitzky S. Synovial cysts of the lumbar spine:diagnosis, surgical management, and pathogenesis. Report of eight cases. Surg Neurol. 1995;43:459–64. - PubMed
-
- Wang YY, McKelvie P, Trost N, Murphy MA. Trauma as a precipitant of haemorrhage in synovial cysts. J Clin Neurosci. 2004;11:436–9. - PubMed
-
- Jabre A, Shahbabian S, Keller JT. Synovial cyst of the cervical spine. Neurosurgery. 1987;20:316–8. - PubMed
-
- Howington JU, Connolly ES, Voorhies RM. Intraspinal synovial cysts:10-year experience at the Ochsner Clinic. J Neurosurg. 1999;91:193–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
