Effects of a proprietary mixture of extracts from Sabal serrulata fruits and Urtica dioica roots (WS® 1541) on prostate hyperplasia and inflammation in rats and human cells
- PMID: 38560358
- PMCID: PMC10979176
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1379456
Effects of a proprietary mixture of extracts from Sabal serrulata fruits and Urtica dioica roots (WS® 1541) on prostate hyperplasia and inflammation in rats and human cells
Abstract
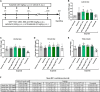
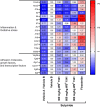
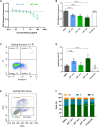
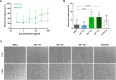
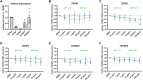
Introduction: Phytotherapeutics, particularly extracts from Sabal serrulata (saw palmetto) fruit or Urtica dioica (stinging nettle) root, are popular for the treatment of male lower urinary symptoms in many countries, but their mechanism of action is poorly understood. We performed in vivo and in vitro studies to obtain deeper insight into the mechanism of action of WS® 1541, a proprietary combination of a Sabal serrulata fruit and an Urtica dioica root extract (WS® 1473 and WS® 1031, respectively) and its components. Methods: We used the sulpiride model of benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats and tested three doses of WS® 1541 in comparison to finasteride, evaluating weight of prostate and its individual lobes as well as aspects of inflammation, oxidative stress, growth and hyperplasia. In human BPH-1 cells, we studied the effect of WS® 1473, WS® 1031, WS® 1541 and finasteride on apoptosis, cell cycle progression and migrative capacity of the cells. Results: WS® 1541 did not reduce prostate size in sulpiride treated rats but attenuated the sulpiride-induced changes in expression of most analyzed genes and of oxidized proteins and abrogated the epithelial thickening. In vitro, WS® 1473 and WS® 1031 showed distinct profiles of favorable effects in BPH-1 cells including anti-oxidative, anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects, as well as inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal-transition. Conclusion: This data supports a beneficial effect of the clinically used WS® 1541 for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms associated with mild to moderate benign prostate syndrome and provides a scientific rationale for the combination of its components WS® 1473 and WS® 1031.
Keywords: BPH-1 cells; PRO 160/120; Sabal serrulata; Urtica dioica; WS® 1541; benign prostate hyperplasia; epithelial-mesenchymal-transition; inflammation.
Copyright © 2024 Sens-Albert, Weisenburger, König, Melcher, Scheyhing, Rollet, Lluel, Koch, Lehner and Michel.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors KR and PL were employed by Urosphere SAS, Parc Technologique Du Canal. Authors CS-A, SW, BK, SM, US, EK, and ML were employed by Dr. Willmar Schwabe GmbH and Co., KG. MC received funding from Dr. Willmar Schwabe GmbH & Co. KG. The funder had the following involvement in the study: Study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, and preparation of the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combined Sabal and Urtica Extracts (WS® 1541) Exert Anti-proliferative and Anti-inflammatory Effects in a Mouse Model of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 29;10:311. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00311. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30984003 Free PMC article.
-
Extracts from fruits of saw palmetto (Sabal serrulata) and roots of stinging nettle (Urtica dioica): viable alternatives in the medical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and associated lower urinary tracts symptoms.Planta Med. 2001 Aug;67(6):489-500. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-16496. Planta Med. 2001. PMID: 11509966 Review.
-
WS PRO 160 I 120 mg (a combination of sabal and urtica extract) in patients with LUTS related to BPH.Ther Adv Urol. 2019 Oct 11;11:1756287219879533. doi: 10.1177/1756287219879533. eCollection 2019 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Urol. 2019. PMID: 31656534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined sabal and urtica extract compared with finasteride in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: analysis of prostate volume and therapeutic outcome.BJU Int. 2000 Sep;86(4):439-42. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2000.00776.x. BJU Int. 2000. PMID: 10971268 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of algerian nettle (Urtica dioica L.) on benign prostatic hyperplasia and their mechanism of action elucidation: in vivo and in silico approaches.Nat Prod Res. 2024 Nov;38(22):4017-4027. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2023.2272283. Epub 2023 Oct 22. Nat Prod Res. 2024. PMID: 37867291
Cited by
-
Project-Based Public-Private Collaborations.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;286:21-31. doi: 10.1007/164_2024_722. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39120768 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

