Laparoscopic pyeloplasty for newborns with severe hydronephrosis
- PMID: 38560400
- PMCID: PMC10979644
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1343211
Laparoscopic pyeloplasty for newborns with severe hydronephrosis
Abstract
Aim: We aimed to investigate the short-term efficacy and safety of laparoscopic pyeloplasty for treating newborns with severe hydronephrosis due to ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO).
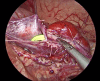
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on 16 newborn patients with severe neonatal hydronephrosis who underwent laparoscopic pyeloplasty at our hospital from January 2021 to November 2022. All patients were regularly followed up. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty with double J stent placement was performed after the presence of severe hydronephrosis was confirmed.
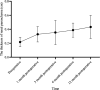
Results: Among the 16 pediatric patients (13 males, 3 females), the left side was affected in 13 cases and the right side in 3. The average age at surgery was 9.50 (8.50-12.00) days, with an average weight of 3.30 ± 0.95 kg. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty was performed in all cases without the need for open conversion. The mean surgery duration was 292.06 ± 73.60 min, with minimal blood loss (2.50, 2.00-5.00 ml). Postoperative hospital stays averaged 13.44 ± 4.70 days. No anastomotic leakage occurred, and follow-ups at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months showed no stent displacement, except for one case where the stent was removed at 1 month, and the others at 3 months. There were no cases of worsened hydronephrosis, except for one with renal atrophy at the 6-month follow-up. Changes in renal pelvis anteroposterior diameter exhibited a time effect (F = 49.281, P < 0.001), with significant differences at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively compared to preoperative values (P < 0.05). Notably, differences were observed between 6 and 3 months, as well as between 12 and 3 months postoperatively (P < 0.05). Similarly, renal parenchymal thickness changes showed a time effect Pediatric urology, Guangdong Women and Children Hospital, Guangzhou, China (F = 49.281, P < 0.001), with significant differences at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively compared to preoperative values (P < 0.05). Significant differences were also noted between 6 and 1 month, as well as between 12 and 1 month postoperatively (P < 0.05). There was one case of urinary tract infection after surgery, and no case of recurrence was observed.
Conclusion: Severe neonatal hydronephrosis must be treated promptly. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty is a safe and feasible treatment with minimal complications for newborn patients with severe hydronephrosis due to UPJO.
Keywords: hydronephrosis; laparoscopy; neonatal period; surgery; ureteropelvic junction.
© 2024 Shi, Lao, Ouyang, Chen, Zhang, Luo and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Use of double-J ureteric stents post-laparoscopic pyeloplasty to treat ureteropelvic junction obstruction in hydronephrosis for pediatric patients: a single-center experience.J Int Med Res. 2020 Apr;48(4):300060520918781. doi: 10.1177/0300060520918781. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32345075 Free PMC article.
-
[Treatment of crossing vessels in laparoscopic pyeloplasty].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019 Aug 18;51(4):660-664. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.04.011. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019. PMID: 31420618 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Laparoscopic pyeloplasty versus open pyeloplasty for recurrent ureteropelvic junction obstruction in children.J Pediatr Urol. 2016 Dec;12(6):401.e1-401.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2016.06.010. Epub 2016 Jul 21. J Pediatr Urol. 2016. PMID: 27614698
-
Outcome of Renal Function after Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty in Children with High-Grade Hydronephrosis.Urol Int. 2023;107(7):666-671. doi: 10.1159/000529032. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Urol Int. 2023. PMID: 36958292 Review.
-
Long-term renal function post-pyeloplasty: a systematic review.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Apr 9. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04495-1. Online ahead of print. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40205125 Review.
References
-
- Sharifian M, Esfandiar N, Mohkam M, Dalirani R, Baban Taher E, Akhlaghi A. Diagnostic accuracy of renal pelvic dilatation in determining outcome of congenital hydronephrosis. Iran J Kidney Dis. (2014) 8(1):26–30. PMID: 24413717. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

