Effectiveness and Safety of Anlotinib Combined with PD-1 Blockades in Patients with Previously Immunotherapy Treated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Exploratory Study
- PMID: 38560413
- PMCID: PMC10979677
- DOI: 10.2147/LCTT.S444884
Effectiveness and Safety of Anlotinib Combined with PD-1 Blockades in Patients with Previously Immunotherapy Treated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Exploratory Study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness and tolerability of anlotinib plus PD-1 blockades in patients with previously immunotherapy treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: A total of 67 patients with previously immunotherapy treated advanced NSCLC who received anlotinib plus PD-1 blockades in clinical practice were screened retrospectively. All the PD-1 blockades used in this study were approved in China and consisted of sintilimab, camrelizumab, tislelizumab and pembrolizumab. Effectiveness and safety of anlotinib plus PD-1 blockades were assessed, and all patients were followed up regularly. Clinical significance between response status to previous immune-related treatment regimens and therapeutic outcomes of anlotinib plus PD-1 blockades was further explored.
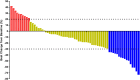
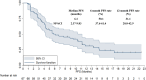
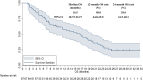
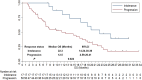
Results: The best overall response among the 67 patients suggested that a partial response was observed in 16 patients, stable disease was noted in 41 patients and progressive disease was found in 10 patients, which yielded an objective response rate of 23.9% (95% CI: 14.3-35.9%) and a disease control rate of 85.1% (95% CI: 74.3-92.6%). Prognostic outcomes indicated that the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.1 months (95% CI: 2.37-9.83) and the median overall survival (OS) was 16.5 months (95% CI: 10.73-22.27). Exploratory analysis highlighted that patients who were intolerant to previous immune-related regimens (17 patients) might have a superior prognosis (median OS: 22.3 months vs 12.5 months, P=0.024). Additionally, adverse reactions with any grades during anlotinib plus PD-1 blockades administration were observed in 62 patients (92.5%), of which 31 patients (46.3%) had ≥grade 3 adverse reactions. Most common adverse reactions were fatigue, hypertension, diarrhea and hepatotoxicity.
Conclusion: Anlotinib plus PD-1 blockades demonstrated promising effectiveness and tolerable safety in patients with previously immunotherapy treated advanced NSCLC. Those who were intolerant to previous immune-related regimens might benefit significantly from treatment with anlotinib plus PD-1 blockades. This conclusion should be confirmed in future studies.
Keywords: PD-1 blockades; anlotinib; effectiveness; previously immunotherapy treated NSCLC; safety.
© 2024 Dou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergizing Success: The Role of Anlotinib Combinations in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 16;18(4):585. doi: 10.3390/ph18040585. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40284020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feasibility and Tolerability of Anlotinib Plus PD-1 Blockades for Patients with Treatment-Refractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Retrospective Exploratory Study.Cancer Manag Res. 2024 Feb 1;16:73-86. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S427680. eCollection 2024. Cancer Manag Res. 2024. PMID: 38318097 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Tolerability of Anlotinib Plus PD-1 Inhibitors for Patients with Previously Treated Metastatic Soft-Tissue Sarcoma.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Sep 28;15:7581-7591. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S379269. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 36196372 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility and Tolerability of Anlotinib Plus PD-1 Inhibitors for Previously-Treated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Exploratory Study.Biologics. 2024 Nov 5;18:313-326. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S489363. eCollection 2024. Biologics. 2024. PMID: 39524378 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety evaluations of anlotinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with bevacizumab.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 27;13:973448. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.973448. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36238567 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Respiratory microbiota diversity as a predictive biomarker for the efficacy of PD‑1 blockades in patients with advanced non‑small cell lung cancer: A retrospective exploratory study.Oncol Lett. 2025 Mar 26;29(5):251. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.14997. eCollection 2025 May. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40201032 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Cadonilimab plus anlotinib in small cell lung cancer with brain metastases.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 17;15:1545101. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1545101. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40746596 Free PMC article.
-
scRNA-seq reveals that VEGF signaling mediates the response to neoadjuvant anlotinib combined with PD-1 blockade therapy in non-small cell lung cancer.J Transl Med. 2025 Apr 25;23(1):478. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06485-4. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40281576 Free PMC article.
-
Synergizing Success: The Role of Anlotinib Combinations in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 16;18(4):585. doi: 10.3390/ph18040585. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40284020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical effectiveness of Anlotinib combined with PD-1 inhibitors in treating advanced non-small-cell lung carcinoma.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Jan 15;17(1):674-684. doi: 10.62347/WKFJ4968. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39959242 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

