Kinesin-7 CENP-E in tumorigenesis: Chromosome instability, spindle assembly checkpoint, and applications
- PMID: 38560520
- PMCID: PMC10978661
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1366113
Kinesin-7 CENP-E in tumorigenesis: Chromosome instability, spindle assembly checkpoint, and applications
Abstract
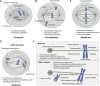
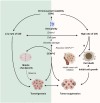
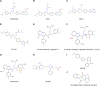
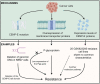
Kinesin motors are a large family of molecular motors that walk along microtubules to fulfill many roles in intracellular transport, microtubule organization, and chromosome alignment. Kinesin-7 CENP-E (Centromere protein E) is a chromosome scaffold-associated protein that is located in the corona layer of centromeres, which participates in kinetochore-microtubule attachment, chromosome alignment, and spindle assembly checkpoint. Over the past 3 decades, CENP-E has attracted great interest as a promising new mitotic target for cancer therapy and drug development. In this review, we describe expression patterns of CENP-E in multiple tumors and highlight the functions of CENP-E in cancer cell proliferation. We summarize recent advances in structural domains, roles, and functions of CENP-E in cell division. Notably, we describe the dual functions of CENP-E in inhibiting and promoting tumorigenesis. We summarize the mechanisms by which CENP-E affects tumorigenesis through chromosome instability and spindle assembly checkpoints. Finally, we overview and summarize the CENP-E-specific inhibitors, mechanisms of drug resistances and their applications.
Keywords: CENP-E; aneuploidy; cancer; chromosome instability; kinesin; tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Wei and She.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Agarwal R., Gonzalez-Angulo A. M., Myhre S., Carey M., Lee J. S., Overgaard J., et al. (2009). Integrative analysis of cyclin protein levels identifies cyclin b1 as a classifier and predictor of outcomes in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 3654–3662. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-3293 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

