Effectiveness of psychoeducational interventions on psychological distress and health-related quality of life among patients with maintenance hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38561244
- PMCID: PMC10986446
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2331613
Effectiveness of psychoeducational interventions on psychological distress and health-related quality of life among patients with maintenance hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To examine the effectiveness of psychoeducational interventions on depression, anxiety, and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) for people undergoing maintenance hemodialysis (MHD).
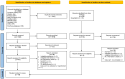
Methods: This review used systematic review and meta-analysis as the research design. Nine databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, CINAHL Complete, Cochrane Library, CNKI, WanFang, VIP, and Chinese Biomedical Literature Database, were searched from the inception to the 8th of July 2023. Two reviewers independently identified randomized controlled trials (RCT) examining the effects of psychoeducational interventions on MHD patients.
Results: Fourteen studies involving 1134 MHD patients were included in this review. The results of meta-analyses showed that psychoeducational intervention had significant short-term (< 1 m) (SMD: -0.87, 95% CI: -1.54 to -0.20, p = 0.01, I2 = 91%; 481 participants), and medium-term (1-3 m) (SMD: -0.29, 95% CI: -0.50 to -0.08, p = 0.01, I2 = 49%; 358 participants) on anxiety in MHD patients, but the effects could not be sustained at longer follow-ups. Psychoeducational interventions can also have short-term (< 1 m) (SMD: -0.65, 95% CI: -0.91 to -0.38, p < 0.00001, I2 = 65%; 711 participants) and medium-term (1-3 m) (SMD: -0.42, 95% CI: -0.76 to -0.09, p = 0.01, I2 = 69%; 489 participants) effects in reducing depression levels in MHD patients. Psychoeducational interventions that use coping strategies, goal setting, and relaxation techniques could enhance the QOL in MHD patients in the short term (< 1 m) (SMD: 0.86, 95% CI: 0.42 to 1.30, p = 0.02, I2 = 86%; 241 participants).
Conclusions: Psychoeducational interventions have shown great potential to improve anxiety, depression, and quality of life in patients with MHD at the short- and medium-term follow-ups.Trial registration number: CRD42023440561.
Keywords: Maintenance hemodialysis; meta-analysis; psychoeducational interventions; quality of life; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
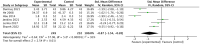


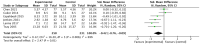

Similar articles
-
Psychological interventions for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Apr 17;4(4):CD006913. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006913.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40243391
-
Psychosocial interventions for men with prostate cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Dec 24;2013(12):CD008529. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008529.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24368598 Free PMC article.
-
Yoga for improving health-related quality of life, mental health and cancer-related symptoms in women diagnosed with breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 3;1(1):CD010802. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010802.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28045199 Free PMC article.
-
Music interventions for improving psychological and physical outcomes in people with cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 12;10(10):CD006911. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006911.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34637527 Free PMC article.
-
Educational interventions for the management of cancer-related fatigue in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 24;11(11):CD008144. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008144.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27883365 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of dyadic psychoeducational interventions for haemodialysis patients and their family caregivers: a randomised controlled trial.BMC Nurs. 2025 Mar 4;24(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-02835-1. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40038667 Free PMC article.
-
A Cross-Sectional Multivariable Analysis of the Quality of Hemodialysis Patients' Life in Lahore City, Pakistan.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Jan 18;13(2):186. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13020186. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857213 Free PMC article.
-
The utility of brief instruments for depression screening in dialysis patients.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Nov 22;18(1):sfae369. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae369. eCollection 2025 Jan. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 39781480 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and Influencing Factors of Demoralization Syndrome in Elderly Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients: A Multi-Center Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Gen Med. 2025 Feb 15;18:787-797. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S511458. eCollection 2025. Int J Gen Med. 2025. PMID: 39974563 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of a psychoeducational nursing program on self-efficacy and psychological adjustment in hemodialysis patients.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 4;15(1):19568. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04052-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40467688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease (GBD) . Global Health Date Exchange[EB/OL]. https://ghdx.healthdata.org/.
-
- Jing C, Jing X, Yanqing J, et al. . Expert consensus on clinical practice of injection safety in hemodialysis. Chi J Nursing. 2022;57(07):785–790.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
