The BKCa (slo) channel regulates the cardiac function of Drosophila
- PMID: 38561252
- PMCID: PMC10984821
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.15996
The BKCa (slo) channel regulates the cardiac function of Drosophila
Abstract
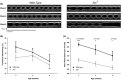
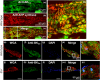
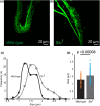
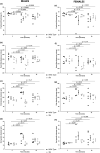
The large conductance, calcium, and voltage-active potassium channels (BKCa) were originally discovered in Drosophila melanogaster as slowpoke (slo). They are extensively characterized in fly models as ion channels for their roles in neurological and muscular function, as well as aging. BKCa is known to modulate cardiac rhythm and is localized to the mitochondria. Activation of mitochondrial BKCa causes cardioprotection from ischemia-reperfusion injury, possibly via modulating mitochondrial function in adult animal models. However, the role of BKCa in cardiac function is not well-characterized, partially due to its localization to the plasma membrane as well as intracellular membranes and the wide array of cells present in mammalian hearts. Here we demonstrate for the first time a direct role for BKCa in cardiac function and cardioprotection from IR injury using the Drosophila model system. We have also discovered that the BKCa channel plays a role in the functioning of aging hearts. Our study establishes the presence of BKCa in the fly heart and ascertains its role in aging heart function.
Keywords: BK channels; antioxidants; life span; mitochondria; potassium channel; reactive oxygen species.
© 2024 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BKCa (Slo) Channel Regulates Mitochondrial Function and Lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster.Cells. 2019 Aug 21;8(9):945. doi: 10.3390/cells8090945. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31438578 Free PMC article.
-
MitoBKCa channel is functionally associated with its regulatory β1 subunit in cardiac mitochondria.J Physiol. 2019 Aug;597(15):3817-3832. doi: 10.1113/JP277769. Epub 2019 Jul 11. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31173379 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Activation of BKCa Channels in Mice Protects Against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury of Isolated Hearts by Modulating Mitochondrial Function.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019 Jan 28;5:194. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00194. eCollection 2018. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019. PMID: 30746365 Free PMC article.
-
BKCa Channels as Targets for Cardioprotection.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Aug 17;9(8):760. doi: 10.3390/antiox9080760. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32824463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Impact of BKCa Channel Function in Cellular Membranes on Cardiac Electrical Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 26;25(3):1537. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031537. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional large-conductance calcium and voltage-gated potassium channels in extracellular vesicles act as gatekeepers of structural and functional integrity.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 2;16(1):42. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55379-4. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39747826 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ancaten‐Gonzalez, C. , Segura, I. , Alvarado‐Sanchez, R. , Chavez, A. E. , & Latorre, R. (2023). Ca(2+)‐ and voltage‐activated K(+) (BK) channels in the nervous system: One gene, a myriad of physiological functions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(4), 3407. 10.3390/ijms24043407 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atkinson, N. S. , Robertson, G. A. , & Ganetzky, B. (1991). A component of calcium‐activated potassium channels encoded by the Drosophila slo locus. Science, 253(5019), 551–555. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

