Reliability and validity of a graphical computerized adaptive test Longshi scale for rapid assessment of activities of daily living in stroke survivors
- PMID: 38561344
- PMCID: PMC10985115
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-57671-1
Reliability and validity of a graphical computerized adaptive test Longshi scale for rapid assessment of activities of daily living in stroke survivors
Abstract
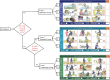
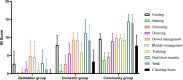
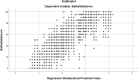
Stroke survivors frequently experience difficulties in daily activities, such as bathing, feeding, and mobility. This study aimed to evaluate the reliability and validity of a computer-adaptive test-Longshi scale (CAT-LS) for assessing activities of daily living (ADL) in stroke survivors. This cross-sectional study collected data using an electronic application. The ADL function of stroke survivors in rehabilitation departments of hospitals was assessed using both the CAT-LS and BI. Correlations between the CAT-LS and Barthel index (BI) and concurrent validity were evaluated using Pearson's correlation test and multiple linear regression. Interrater reliability was evaluated using the intraclass correlation coefficient based on a two-way random effect. The internal consistency of the CAT-LS was assessed using Cronbach's coefficient (α) and corrected item-total correlations. Overall, 103 medical institutions in China were used in this study. In total, 7151 patients with stroke were included in this study. The CAT-LS classified patients into three ADL groups (bedridden, domestic, and community) with significantly different BI scores (P < 0.05). The CAT-LS results obtained using the decision-tree scoring model were consistent with the scores for each BI item. A strong correlation was observed between CAT-LS and BI (Pearson's r: 0.6-0.894, P < 0.001). The CAT-LS demonstrated good internal consistency (Cronbach's α, 0.803-0.894) and interrater reliability (ICC, 0.928-0.979). CAT-LS is time-efficient and requires < 1 min to administer. The CAT-LS is a reliable and valid tool for assessing ADL function in stroke survivors and can provide rapid and accurate assessments that reduce the burden on healthcare professionals. Further validation of this tool in other populations and settings is necessary.Study registration number: No.: ChiCTR2000034067; http://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=54770 .
Keywords: Activities of daily living; Barthel index; Computer adaptive test-Longshi Scale; Stroke.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of the Longshi scale in assessment of function in patients from different economic, educational and regional backgrounds in China.Clin Rehabil. 2023 Nov;37(11):1552-1558. doi: 10.1177/02692155231174689. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Clin Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 37309131
-
Reliability of Longshi scale with remote assessment of smartphone video calls for stroke patients' activities of daily living.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2023 Mar;32(3):106950. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2022.106950. Epub 2022 Dec 19. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2023. PMID: 36542891
-
Development of a computerized adaptive test for assessing activities of daily living in outpatients with stroke.Phys Ther. 2013 May;93(5):681-93. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20120173. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Phys Ther. 2013. PMID: 23329557
-
Reliability and responsiveness of the activities of daily living computerized adaptive testing system in patients with stroke.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 Nov;95(11):2055-63. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2014.04.025. Epub 2014 May 17. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014. PMID: 24845220
-
Examination of reliability and validity of the Self-Assessment Burden Scale-Motor for community-dwelling older adults in Japan: a validation study.PeerJ. 2024 Jul 18;12:e17730. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17730. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39035163 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between serum albumin and severe impairment of activities of daily living in patients with stroke: a cross-sectional study.Front Neurol. 2025 Jan 6;15:1501294. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1501294. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39835151 Free PMC article.
-
Estimates of multidimensional poverty and its determinants among older people in rural China: evidence from a multicenter cross-sectional survey.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Oct 15;24(1):835. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05413-3. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 39407115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Winstein CJ, Stein J, Arena R, Bates B, Cherney LR, Cramer SC, Deruyter F, Eng JJ, Fisher B, Harvey RL, et al. Guidelines for adult stroke rehabilitation and recovery: A guideline for healthcare professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2016;47:e98–e169. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000098. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Edemekong, P. F. et al. Activities of daily living. In Starters (2022).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous